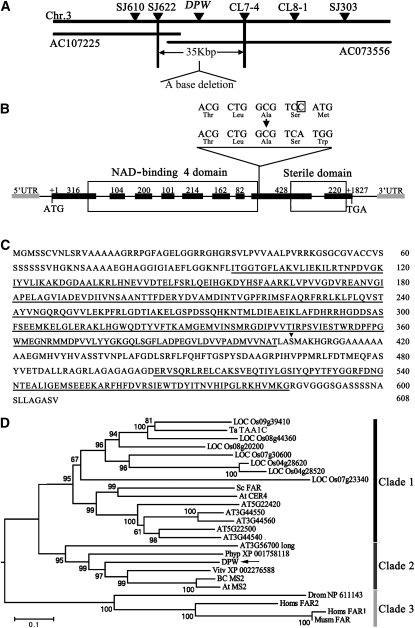
Figure 5.
Molecular Identification and Sequence Analysis of DPW.
(A) Fine mapping of the DPW gene on chromosome 3. The names and positions of the molecular markers are indicated. AC107225 and AC073556 are genomic DNA accession numbers. The DPW locus was mapped to a 35-kb region between two molecular markers (SJ622 and CL7-4).
(B) A schematic representation of the exon and intron organization of DPW. The mutant sequence has one base deletion in the eighth exon, which is boxed. +1 Indicates the starting nucleotide of translation (ATG), and +1827 indicates the stop codon (TAG). Black boxes indicate exons, intervening lines indicate introns, gray boxes indicate 5′-UTR and 3′-UTR, respectively, and the white boxes indicate the NAD binding 4 domain and male sterility domain.
(C) The DPW protein sequence. The NAD binding 4 domain and sterile domain are underlined. The black triangle shows the position of base deletion.
(D) A neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree summarizes the evolutionary relationships among the DPW-related proteins (E value of BLASTP result is <1E-11). The proteins are named according to their gene names or NCBI accession numbers: ABO14927 (BC MS2), AT3G11980 (At MS2), AAD38039 (Sc FAR), CAD30692 (Ta TAA1C), AT4G33790 (At CER4), NP_060569 (Homs FAR2), NP_115604 (Homs FAR1), and NP_081655 (Musm_FAR). The numbers under the branches refer to the bootstrap value of the neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree. The length of the branches is proportional to the amino acid variation rates. At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Ta, Triticum aestivum; Sc, Simmondsia chinensis; BC, Brassica rapa subsp chinensis; Vitv, Vitis vinifera; Phyp, Physcomitrella patens subsp patens; Homs, Homo sapiens; Musm, Mus musculus; Drom, Drosophila melanogaster. The bar indicates the estimated number of amino acid substitutions per site (for alignment, see Supplemental Figure 4 and Supplemental Data Set 1 online).