Fig. 2.
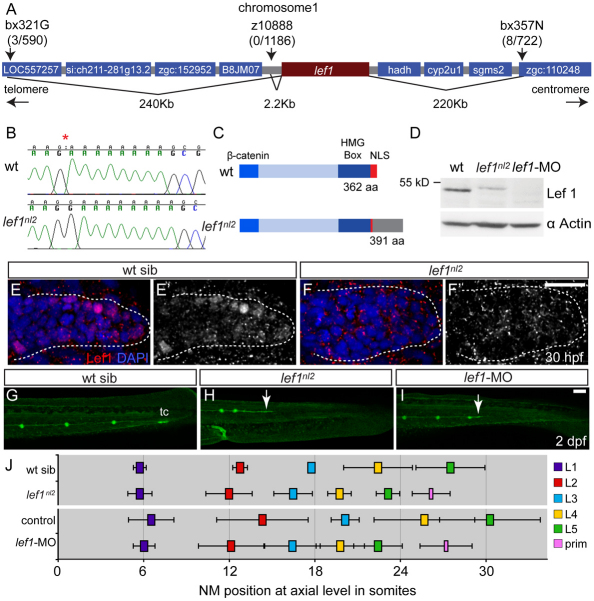
The lef1nl2 mutant contains a lesion in the lef1 gene. (A) The lef1nl2 mutation was mapped to a 460 Kb region on chromosome 1. Numbers of recombinants are indicated under each marker. (B) The lef1nl2 mutation is a single guanine insertion at position 1120 (red asterisk). (C) The resulting frame shift is predicted to disrupt the nuclear localization signal (NLS) and extend the protein by 29 amino acids (aa; also shown a β-catenin binding domain and HMG Box). (D) Western blot of wild-type, lef1nl2 mutant and lef1 morphant whole embryo lysates probed with anti-Lef1 antibody and anti-α actin antibody. (E-F′) Immunolabeling using anti-Lef1 antibody revealed nuclear labeling (red) in wild-type sibling and cytoplasmic labeling in lef1nl2 mutant embryos. Nuclei are labeled with DAPI. (G-I) Wild-type sibling, lef1nl2 mutant and lef1-MO injected embryos expressing the Tg(–8.0cldnb:lynGFP) transgene at 2 dpf. (G) The pLL was truncated prematurely (white arrows) in the lef1nl2 mutant (H) and lef1 morphant (I). (J) The axial positions of the deposited NMs are shifted anteriorally in lef1nl2 mutants when compared with wild-type siblings and in lef1 morphants when compared with uninjected controls. (Data presented as mean±s.d.; n=6-11 P<0.001, two-way ANOVA with replication.) Scale bars: 50 μm.