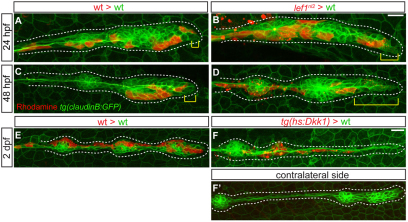
Fig. 8.
Lef1 is required to maintain progenitor cell identity. (A-D) Confocal projections of Tg(–8.0cldnb:lynGFP)-positive, mosaic embryos containing either wild-type or lef1nl2 donor cells (red) at 24 and 48 hpf. (A) Wild-type host primordium at 24 hpf with wild-type donor cells in the leading region (yellow bracket). (B) Chimeric primordium containing lef1nl2 mutant cells in the leading region at 24 hpf (yellow bracket). At 48 hpf, wild-type donor cells remain in the leading region (C; yellow bracket), whereas lef1nl2 cells have moved out of the leading region (D; yellow bracket). (E-F′) Confocal projections of chimeric primordia containing wild type Tg(hsp70l:dkk1-GFP) donor cells. Embryos were heat-shocked at 28 hpf. (E) Primordium containing wild-type cells and a characteristic rounded morphology. (F) Wild-type primordium containing Tg(hsp70l:dkk1-GFP) donor cells shows loss of primordium organization. (F′) Contralateral side of the chimera shown in F is normal. Scale bars: 20 μm.