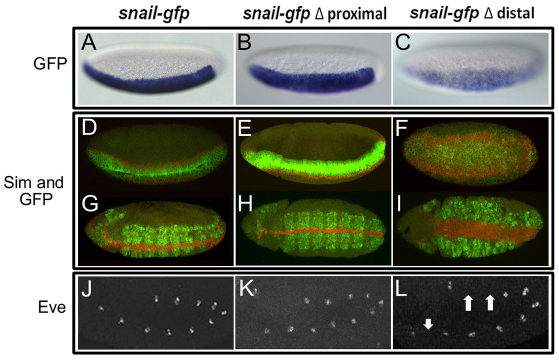
Fig. 2.
The distal CRM is required to rescue gastrulation and Eve cell specification defects. (A-C) In situ hybridization of cellularized wild-type embryos (stage 5) containing sna-gfp construct using a gfp riboprobe and alkaline phosphatase staining procedure. sna-gfp (A) and sna-gfp ΔProximal (B) constructs supported sharp lateral and posterior borders, whereas the sna-gfp ΔDistal (C) construct was weaker and exhibited expanded lateral and posterior boundaries. (D-I) Fluorescent in situ hybridizations of sna1/sna18 mutant embryos using sim (red) and gfp (green) riboprobes to detect sna construct reporter expression and effects on gastrulation through assay of sim. sna mutant embryos containing either the full-length construct sna-gfp (D,G); the proximal delete construct sna-gfp ΔProximal (E,H); or the distal delete construct sna-gfp ΔDistal (F,I) are shown. (J-L) Eve expression in sna mutant germ-band elongated embryos containing sna-gfp (J), sna-gfp ΔProximal (K) or sna-gfp ΔDistal (L). Arrows indicate gaps in eve expression. (See Fig. S1 in the supplementary material for sna-gfp `D to P' and `squish images', also see Fig. S2 in the supplementary material for late Eve expression.)