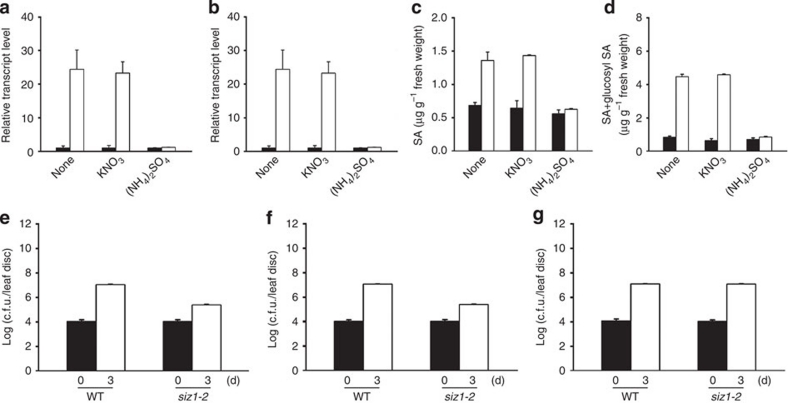
Figure 8. Recovery of SA content and disease resistance to bacterial pathogens of siz1-2 plants to WT levels by exogenous ammonium.
The effect of nitrate or ammonium on transcript levels of the pathogenesis-related genes PR1 and PR2 was examined. Total RNAs were isolated from the leaves of WT and siz1-2 plants grown for 15 days with 5 mM KNO3 or (NH4)2SO4. The transcript levels of PR1 (a) and PR2 (b) were examined by real-time RT–PCR. Their transcript levels in the siz1-2 plants recovered to WT levels with (NH4)2SO4 treatment. Black and white bars indicate WT and siz1-2, respectively. Levels of free and glucosyl SA were evaluated in the leaves of 15-day-old WT and siz1-2 plants grown with 5 mM KNO3 or (NH4)2SO4 in soil. Samples were collected, and then SA and glucosyl SA were extracted using a methanol-based method. Free SA (c) or total SA (d) content combined with free SA and glucosyl SA were analysed with high-performance liquid chromatography. SA levels in the siz1-2 plants recovered to WT levels with (NH4)2SO4 treatment. Results are expressed as means±s.d. (n=3). Black and white bars indicate WT and siz1-2, respectively. (e–g) Effect of nitrate or ammonium on bacterial pathogen infection in siz1-2 plants was also investigated. Fifteen-day-old WT and siz1-2 plants grown in soil treated with 5 mM KNO3 or (NH4)2SO4 were infected with P. syringae DG3 at OD600=0.0001. The samples were collected after 3 days. The bacterial concentration was examined in leaves of WT and siz1-2 plants. (e) Non-treated WT and siz1-2 mutants. (f) KNO3-treated WT and siz1-2 mutants. (g) (NH4)2SO4-treated WT and siz1-2 mutants. The amount in (NH4)2SO4-treated siz1-2 plants recovered to WT amounts. Values of colony-forming units (c.f.u.) represent mean±s.d. (n=8).