Table IV.
Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters of the Parent Drug and Its Active Metabolite for the Model Without and With the Genetic Covariate
| Without the genetic covariate | With the genetic covariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 101) | (N = 99) | |||
| f | 1.00 | – | 1.00 | – |
| β f,D a (nmol−1) | −0.02 | 28 | −0.02 | 24 |
| F ap | 0.85 | 2 | 0.87 | 2 |
| β Fp,D a (nmol−1) | −0.04 | 29 | −0.06 | 27 |
| K a (h−1) | 8.06 | – | 8.06 | – |
| V a (L) | 19.2 | 4 | 19.4 | 5 |
| CL apo (L h−1) | 0.84 | 11 | 0.67 | 11 |
| CL apm (L h−1) | 1.94 | 5 | 2.09 | 5 |
| CL amo (L h−1) | 0.46 | 6 | 0.50 | 7 |
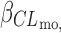 CY P 2D6
a (log(L h−1))
CY P 2D6
a (log(L h−1)) |
− | − | −0.42 | 40 |
| CL amp (L h−1) | 0.09 | 12 | 0.09 | 12 |
| ω f a | 0.25 | 13 | 0.27 | 12 |
| ω Ka a | 1.50 | 21 | 1.41 | 25 |
| ω V a | 0.19 | 18 | 0.26 | 13 |
| ωCL apo | 0.52 | 29 | 0.46 | 38 |
| ωCL amo | 0.51 | 8 | 0.50 | 8 |
| γCL apo | 0.79 | 12 | 0.82 | 12 |
| b p | 0.31 | 3 | 0.30 | 3 |
| a m (nmol−1) | 66.9 | 14 | 66.5 | 14 |
| b m | 0.06 | 9 | 0.06 | 9 |
Estimates and relative standard errors (in grey,%) using the SAEM algorithm in MONOLIX and encoding in closed form
V = V p = V m
ω Between-subject standard deviation, γ within-subject standard deviation, a additive coefficient in nanomoles per liter, b multiplicative coefficient, a p was fixed to 0
aEstimates that rely on the assumption that V m = V p
