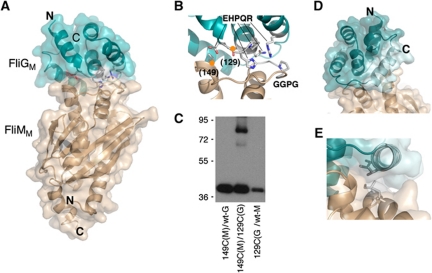
Figure 2.
Structure of the T. maritima FliMM:FliGM complex. (A) Overall shape of the complex. The N- and C-termini of FliMM are oriented towards the bottom in this view; these parts of FliM are directed towards the bottom of the C-ring in the flagellar basal body (Park et al, 2006; Sarkar et al, 2010b). (A stereo version of this figure is provided in Supplementary data.) (B) The FliGM:FliMM interface. The EHPQR residues of FliG and the GGXG motif of FliM are indicated. Orange circles mark positions where Cys residues were introduced to confirm the interaction by crosslinking. Numbers are for the E. coli protein. Unbiased electron density for the EHPQR and GGXG motifs is shown in Supplementary data. (C) Crosslinking through the introduced Cys residues. Crosslinking was induced using Cu-phenanthroline. (D) Packing of the helix near the C-terminus of FliGM against the body of the domain. The helix is shown in lighter colour. In the previous crystal structure of FliGMC (Brown et al, 2002), this helix is detached from the domain and makes extensive inter-subunit crystal contacts instead. (E) Hydrophobic contacts between the helix and FliMM that stabilize the close-packed conformation of the helix.