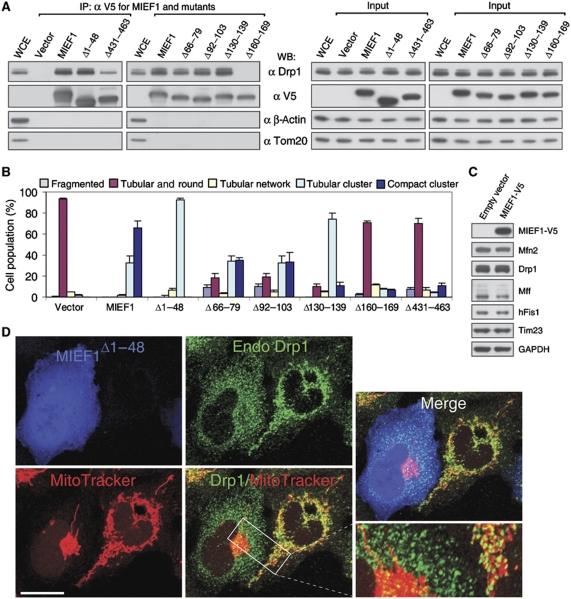
Figure 6.
MIEF1's interaction with Drp1 rather than its mitochondrial localization is crucial for the MIEF1-induced mitochondrial fusion phenotype. (A) Cell lysates of 293T cells transfected with empty vector, wild-type and various mutants of MIEF1-V5, as indicated, were immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 agarose, and the precipitated complexes were analysed by western blot (WB). WCE, whole cell extract from non-transfected cells. Note that the MIEF1Δ160−169 mutant does not bind Drp1 and that the MIEF1Δ431−463 mutant binds only weakly. (B) Percentages (mean±s.e.m.) of cells with indicated mitochondrial morphologies in 293T cultures transfected with empty vector (n=582), wild-type MIEF1-V5 (n=815), MIEF1Δ1−48 (n=302) MIEF1Δ66−79 (n=455), MIEF1Δ92−103 (n=481), MIEF1Δ130−139 (n=517), MIEF1Δ160−169 (n=663) as well as MIEF1Δ431−463 (n=495) plasmids. Data were from three independent experiments. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of Drp1, hFis1, Mff, Mfn2 and Tim23 in 293T cells transfected with empty vector and MIEF1-V5. (D) Confocal images show that overexpression of MIEF1Δ1−48, which was cytoplasmically located due to lack of the TM domain but retained the ability to bind Drp1, resulted in reduced distribution of Drp1 in mitochondria compared to in the adjacent non-transfected 293T cells. Bar, 20 μm.