Table 1.
Measures of Glycemic Variability with the Equations for Glucose Measurements
| Measure | Formulae | Variables |
|---|---|---|
| M-value*15 | 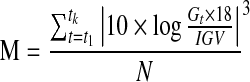 |
G=glucose measured |
| IGV=ideal glucose value | ||
| k=total number of observations | ||
| N=total number of readings | ||
| MAGE16 | 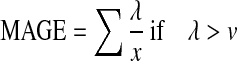 |
λ=blood glucose changes from peak to nadir |
| x=number of valid observations | ||
| v=1 SD of mean glucose for a 24-h period | ||
| Lability Index17 | 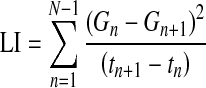 |
G=glucose measured |
| N=total number of readings in a week | ||
| t=time | ||
| ADRR*18 | 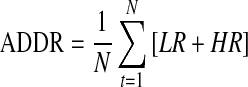 |
N=total number of readings |
| LR=risk value attributed to low glucose | ||
| HR=risk value attributed to high glucose | ||
| J-Index19 | J=0.324×(MBG+SD)2 | MBG=mean glucose levels |
| SD=SD of glucose levels | ||
| LBGI/HBGI*20 | 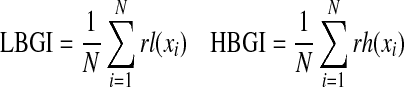 |
N=number of readings |
| rl=risk value associated with a low glucose (if x<0) | ||
| rh=risk value associated with a high glucose (if x>0) | ||
| x=nonlinear transformation of glucose measured | ||
| CONGA21 |
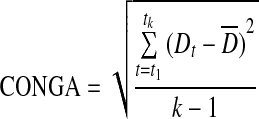 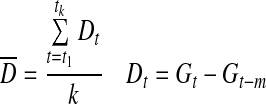
|
k=number of observations with an observation n×60 min ago |
| m=n×60 | ||
| G=glucose measured | ||
| MODD22 | 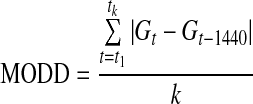 |
k=number of observations with an observation 24 h ago |
| G=glucose measured | ||
| t=time (in min) | ||
| GRADE*23 | GRADE=median(425×{log[log(Gn)]+0.16}2) | G=glucose measured |
| MAG24 | 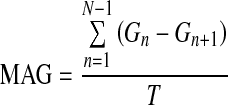 |
G=glucose measured |
| N=number of glucose measurements | ||
| T=total time (in h) |
Glucose was measured in mmol/L.
Indicates methods that assess the quality of glycemia. Three of the measures defined good control in people with type 2 diabetes: M-value, 0≤M≤18 is good control, 19≤M≤31 is fair control, and 32≤M is poor control; J-Index, 10≤J≤20 is ideal control, 20<J≤30 is good control, 30<J≤40 is poor control, and J>40 is lack of control; and Glycemic Risk Assessment in Diabetes Equation (GRADE), median GRADE <5 is good control.
ADRR, average daily risk ratio; CONGA, continuous overlapping net glycemic action; HBGI, High Blood Glucose Index; LBGI, Low Blood Glucose Index; LI, Lability Index; MAG, mean absolute glucose; MAGE, mean amplitude of glucose excursions; MODD, mean of daily differences.
