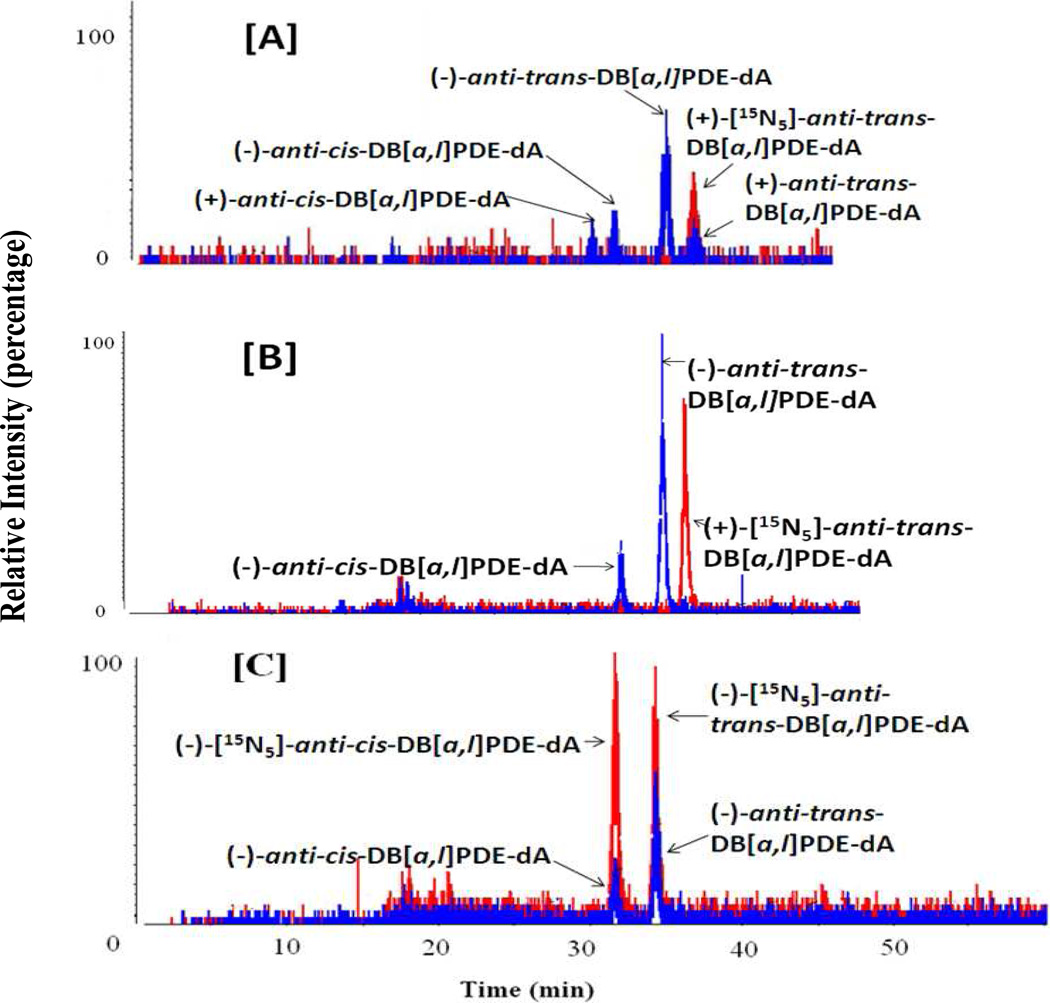
Figure 1.
Representative chromatograms of anti-DB[a,l]PDE-dA adducts obtained from stable isotope dilution HPLC-MS/MS analysis of DNA isolated from oral tissues (soft tissues of the oral cavity, including buccal mucosa, floor of the mouth as well as soft tissues attached to the hard palate were collected and pooled together for DNA adduct analysis) with (±)-DB[a,l]PDE (12 nmol and sacrificed at 48 h after) (A), of mice treated with DB[a,l]P (240 nnol per day for 2 days, sacrificed at 24 h after treatment) (B), and of mice treated with DB[a,l]P (24 nmol, 3 times per week, for 5 weeks, and sacrificed at 48 h after the last dose of carcinogen administration) (C). Peaks in red represent the added internal standard (+)-anti-trans-DB[a,l]PDE-[15N5]-dA adduct. Adducts detected in vivo are shown in blue.