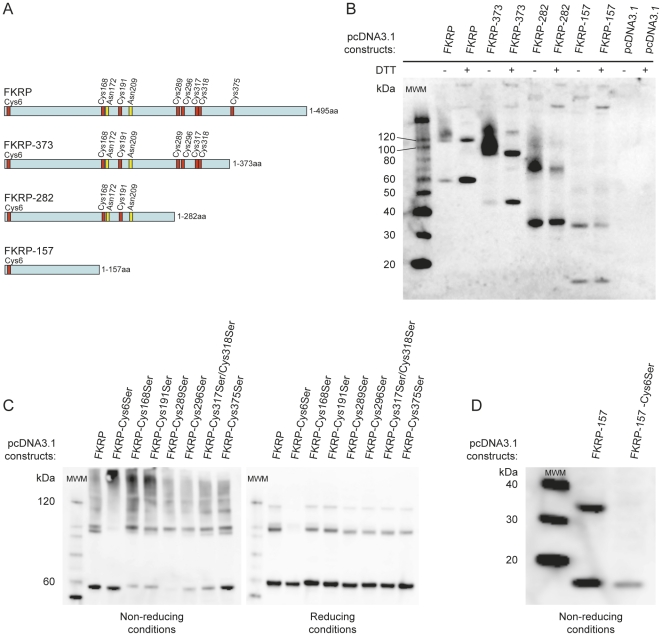
Figure 5. FKRP homodimer formation depends on a Cys6-Cys6 disulfide bridge.
A) Schematic presentation FKRP C-terminal deletion constructs. FKRP-373, FKRP-282 and FKRP-157 denote the length (aa) of the mutant construct. Red vertical bars show Cys (C) positions whereas yellow vertical bars indicate the positions of putative N-glycosylation sites Asn-X-Thr/Ser (N-X-T/S). In the following experiments COS-7 cells were transfected with various pcDNA3.1 constructs and cleared lysates were prepared 48 hrs post transfection in the presence of 5 mM NEM. In all these experiments FKRP was detected with primary antibody FKRP207. B) Cleared lysates from FKRP C-terminal deletion mutants were either left untreated or subjected to reduction (400 mM DTT, at RT for 30 min), followed by (4–12%) SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. C) Cleared lysates from FKRP Cys→Ser substitution mutants were either left untreated (left panel) or subjected to reduction (400 mM DTT, at RT, for 30 min) (right panel), followed by (4–12%) SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. Differences in migration between monomeric forms as well as between dimeric forms (5C) likely represent different FKRP conformations resolved by SDS-PAGE. Such conformational differences might be induced by Cys→Ser mutations as some of the mutant Cys residues must be expected to be involved in intra-molecular disulfide bridges. D) COS-7 lysates from deletion construct FKRP-157, and the Cys6Ser mutant thereof, were subjected to SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions, followed by Western blot analysis.