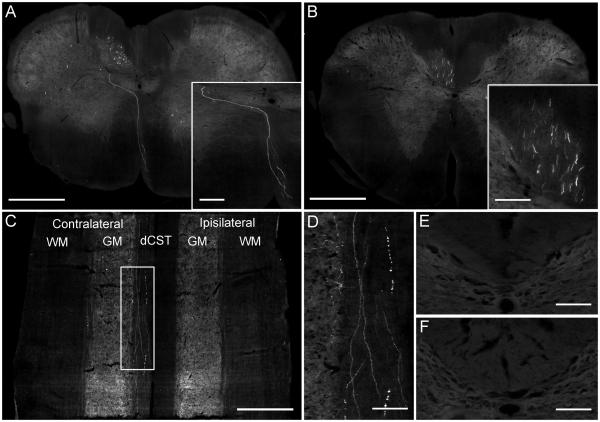
Figure 6.
GFP-positive fibres in the dCST of the cervical spinal cord. (A) The spinomedullary junction of an AAV1 injected rat showing a GFP-positive fibre decussating from the ipsilateral ventral medullary pyramid across the midline and dorsally to the contralateral dCST. Scale bar: 500 μm. Inset shows a higher-magnification image of the decussating GFP-positive fibre. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Numerous GFP-positive fibres are observed in the contralateral dCST at spinal level C1 of an AAV1 injected rat. Scale bar: 500 μm. Inset shows a higher-magnification image of the GFP-positive fibres in the dCST. Scale bar: 150 μm. (C) Cervical spinal cord from an AAV1 injected rat, sectioned in the horizontal axis at the level of the dCST, reveals GFP-positive fibres running the length of the section in the contralateral dCST. WM: White matter; GM: Gray matter. Scale bar: 500 μm. (D) Higher-magnification image of box in (C) shows GFP-positive fibres running through the dCST and collaterals entering the grey matter. Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) No GFP-positive fibres were observed in the dCST of the thoracic spinal cord. Scale bar: 150 μm. (F) No GFP-positive fibres were seen in the dCST of the lumbar spinal cord. Scale bar: 150 μm.