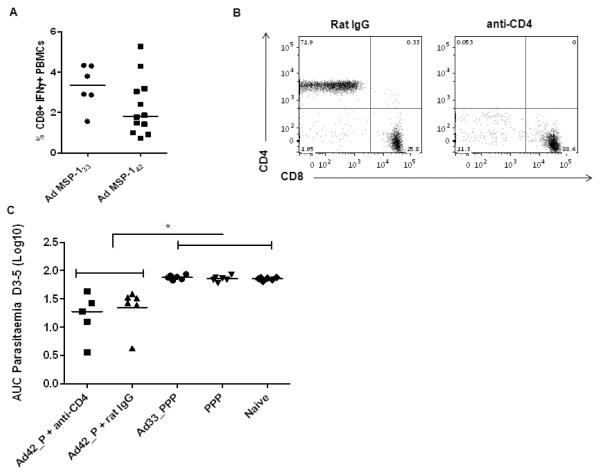
Figure 8. Improved efficacy of AP regimes following P. yoelii blood-stage challenge is not CD4+ T cell dependent.
BALB/c mice (n = 6 / group) were immunized i.m. with either 1.5 μg of P. yoelii MSP-119-GSTprotein in Adju-Phos® three weeks apart (PPP), or primed with 1 × 1010 vp of AdHu5-PyMSP-142 (Ad42) and boosted eight weeks later with 1.5 μg of P. yoelii MSP-119-GSTprotein in Adju-Phos®. One group of mice immunized with the AP Adju-Phos® regime was depleted of CD4+ T cells, the other received normal rat IgG as a control. Separately BALB/c mice (n = 6 / group) were primed i.m. with 1 × 1010 vp of AdHu5-PyMSP-133 (Ad33) and boosted with three shots of 1.5 μg of P. yoelii MSP-119-GSTprotein in Adju-Phos® three weeks apart. All mice were challenged with 105 pRBCs i.v. two weeks after the final immunization and parasitemia was measured as the percentage of infected red blood cells over time. (A) The percentage of CD8+ IFN-γ+ T cells was measured by ICS in the PBMC of mice two weeks after the AdHu5 vaccines. Median responses are shown. (B) Representative flow plots from one depleted and control mouse showing the percentage of single and double CD3+ CD4+ and CD3+ CD8+ positive cells. (C) AUC analysis of parasitemia. * p<0.05 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison post-test. Median and individual responses are shown.