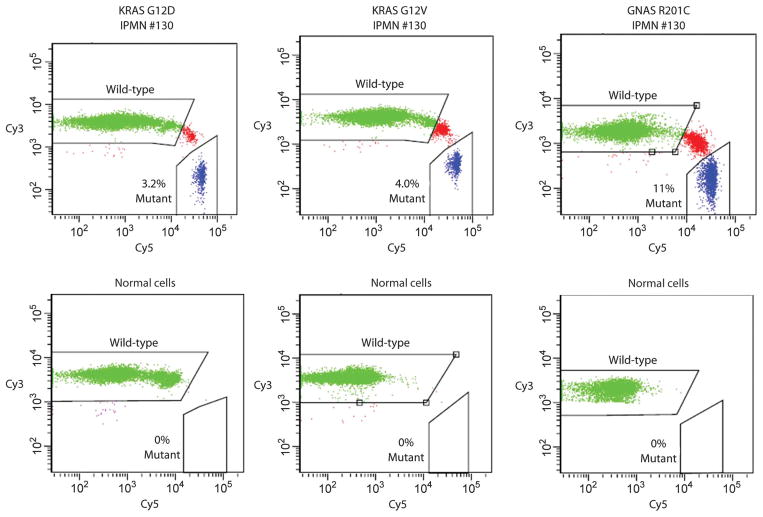
Fig. 3.
BEAMing assays used to quantify mutant representation. PCR was used to amplify KRAS or GNAS sequences containing the region of interest (KRAS codon 12 and GNAS codon 201). The PCR products were then used as templates for BEAMing, in which each template was converted to a bead containing thousands of identical copies of the templates (34). After hybridization to Cy3- or Cy5-labeled oligonucleotide probes specific for the indicated wild-type or mutant sequences, respectively, the beads were analyzed by flow cytometry. Scatter plots are shown for templates derived from the DNA of IPMN 130 or from normal spleen. Beads containing the wild-type or mutant sequences are widely separated in the scatter plots, and the fraction of mutant-containing beads are indicated. Beads whose fluorescence spectra lie between the wild-type– and the mutant-containing beads result from inclusion of both wild-type and mutant templates in the aqueous nanocompartments of the emulsion PCR. See Materials and Methods for details.