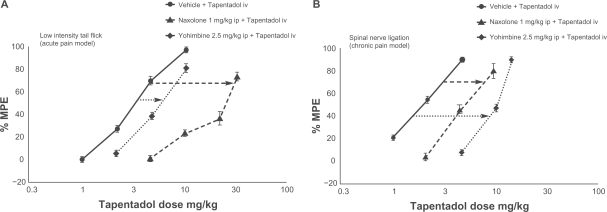
Figure 1.
Differential contribution of μ-opioid agonism and noradrenaline reuptake inhibition in acute and chronic neuropathic pain models.30 In acute pain, antagonizing μ-opioid agonism with naloxone moves the dose–response curve further to the right than antagonizing noradrenaline reuptake inhibition with yohimbine, showing that μ-opioid agonism makes a greater contribution to the compound’s analgesic effect. In chronic neuropathic pain, the opposite is true; noradrenaline reuptake inhibition contributes more to analgesia.
Reprinted from European Journal of Pain, vol 14, issue 8. Schröder W, De Vry J, Tzschentke TM, Jahnel U, Christoph T. Differential contribution of opioid and noradrenergic mechanisms to the antinociceptive and antihypersensitive efficacy of tapentadol in rat models of nociceptive and neuropathic pain, 814–821, Copyright (2010), with permission from Elsevier.
Abbreviation: MPE, maximum possible effect.