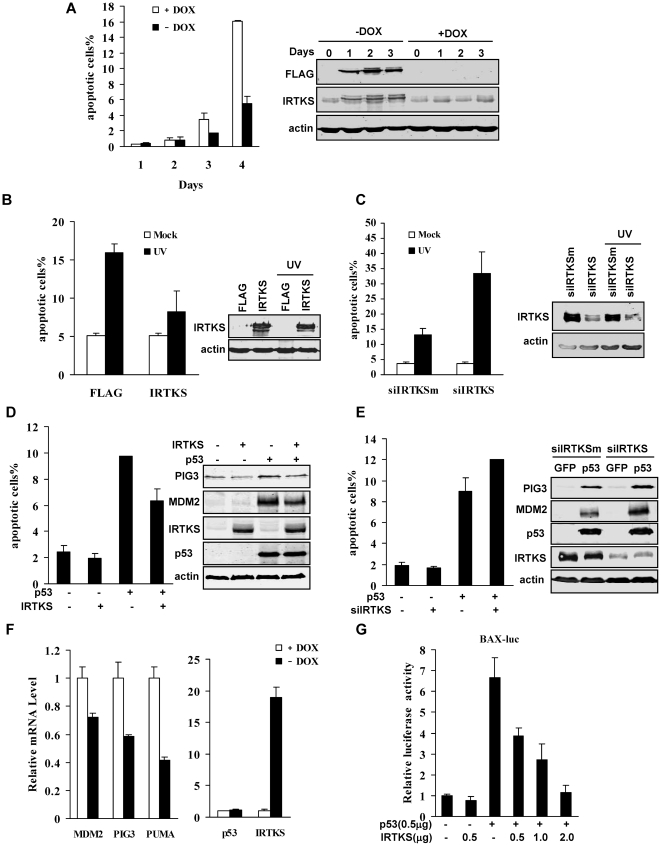
Figure 1. IRTKS suppressed p53-induced apoptosis and transactivation activity.
(A) IRTKS inhibited cell death triggered by serum starvation. The IRTKS Tet-off HT1080 cells were cultured in serum-free medium in the presence or absence of doxycycline (DOX, 10 ng/ml). The cells were collected and analysed by FACS after staining with propidium iodide (PI) at the indicated time. The sub-G1 population was counted as the percentage of cell death. The inducible expression of flag-tagged IRTKS was assessed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG and anti-IRTKS antibodies (right panel). (B, C) IRTKS inhibited UV-induced apoptosis. HT1080 cells with overexpression (B) or knockdown (C) of IRTKS were exposed to UV irradiation and analyzed for apoptosis by Annexin V-FITC/PI (propidium iodide) staining. Representative results of four independent experiments were shown. P<0.005. The expression of IRTKS was assessed by Western blotting (right panel). (D) Overexpression of IRTKS inhibited p53-induced apoptosis. SAOS-2 cells infected with adenoviruses for IRTKS or/and p53 overexpression were analyzed with PI staining by FACS. Data were shown as mean ± s.d. (n = 3), p<0.01. The expression of p53, IRTKS and p53 inducible gene products (PIG3 and MDM2) were analyzed by Western blotting (right panel). (E) Knockdown of IRTKS enhanced p53-induced apoptosis. SAOS-2 cells were treated with IRTKS-siRNA for 24 h, then infected with Ad-p53 or control virus Ad-GFP, and analyzed for apoptosis. Data were shown as mean ± s.d. (n = 3), p<0.01. The expression of p53, IRTKS and p53 inducible gene products (PIG3 and MDM2) were analyzed by Western blotting (right panel). (F) IRTKS inhibited the expression of p53-inducible genes. Total RNA from the IRTKS Tet-off HT1080 cells in the presence (10 ng/ml) or absence of doxycycline was subjected to real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis. Data were expressed as mean ± s.d. (n = 3). p<0.01. (G) IRTKS decreased the transactivation of p53. p53 transactivation activity on the BAX promoter was measured by luciferase reporter gene assay in SAOS-2 cells.