Figure 3.
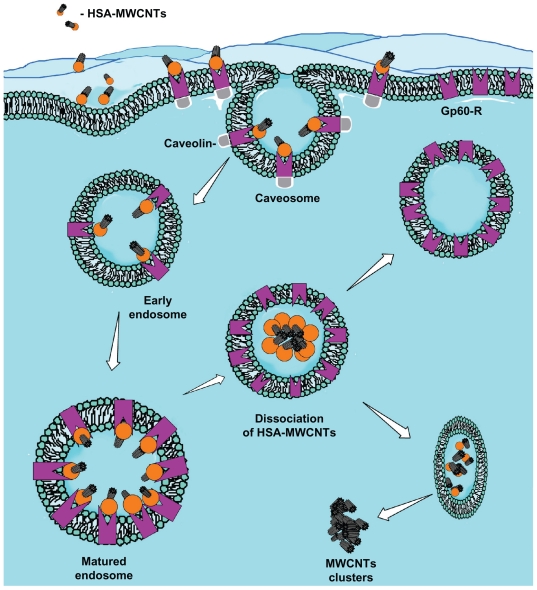
The proposed mechanism for albumin receptor mediated internalization of HSA-MWCNT inside HepG2 cells (schematic drawing). MWCNT internalization involves the selective uptake of HSA-MWCNT with the aid of albumin (GP60) receptors. This usually begins with the formation of caveolar invaginations on the plasma membrane surface. These pits are called caveosomes. The vesicles then transform into early endosomes. Matured (late) endosomes receive internalized material en route to lysosomes, usually from early endosomes in the endocytic pathway and most of the associated receptors circulate back to the cell membrane. Late endosomes mediate a final set of sorting events prior to delivery of material to lysosomes. Lysosomes are the last compartment of the endocytic pathway. The MWCNTs are released inside the cytoplasm forming clusters and HSA is digested by lysosomes.
Abbreviations: Ab, antibody; HSA, human serum albumin; MWCNT, multiwalled carbon nanotube.