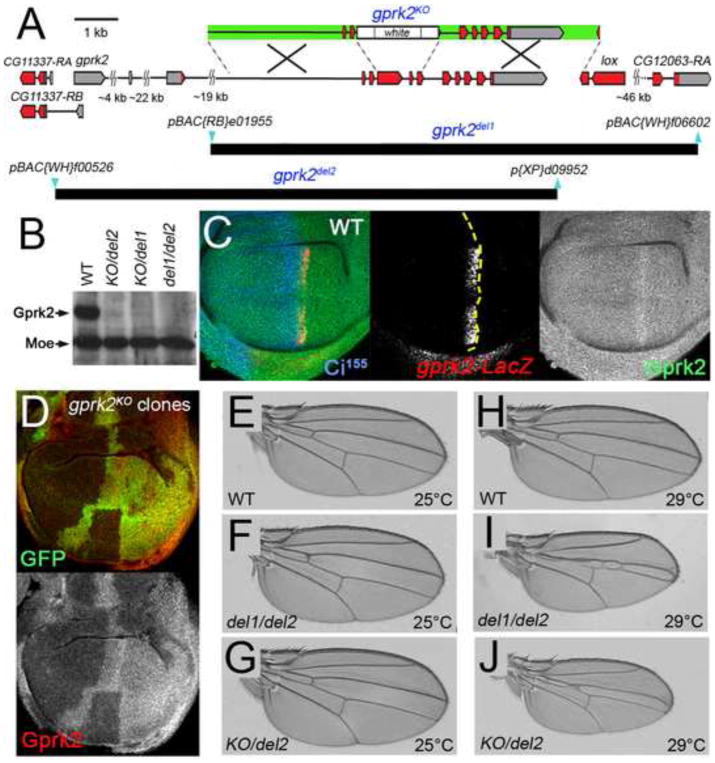
Fig. 1. Generation and characterization of gprk2 null alleles.
(A) Map of the gprk2 locus and defined deletions. The relative positions of non-coding (grey) and coding (red) exons of gprk2, the upstream neighbouring gene CG11337, and two downstream genes (lox and CG12063) are indicated. Two additional genes (CG11333 and CG11334) situated between lox and CG12063 are not shown. A schematic of the targeting construct used to generate the gprk2KO allele is shown above the map (arms of homology in green). The positions of the piggyBac insertions (blue) used to make the gprk2del1 and gprk2del2 alleles and extents of the resulting deletions (black) are shown below. (B) Western blot analysis of wing disc lysates prepared from wild-type, grpk2KO/gprk2del2, grpk2KO/gprk2del1, and grpk2del1/gprk2del2 third-instar larvae. Gprk2 protein is absent from the mutants. The blot was also probed with an anti-Moesin antibody as a loading control. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of a wild-type wing disc to detect Gprk2 (green), nuclear β-galactosidase expressed from a gprk2-LacZ enhancer trap (red), and Ci155 (blue). In this and all subsequent figures, discs are oriented with dorsal up and posterior to the right. Gprk2 protein is detected throughout the disc. The levels of both gprk2 enhancer trap activity and Gprk2 protein are upregulated in anterior cells abutting the A/P compartment boundary (yellow dotted line, as determined by the boundary of Ci immunostaining). (D) Immunofluorescence staining of a wing disc with homozygous gprk2KO clones, marked by the absence of GFP (green). Gprk2 staining (red) is strongly reduced in the clones. (E to J) Wings of flies raised at 25°C (E-G) or 29°C (H–J). Genotypes are: (E,H) wild-type (w1118); (F,I) gprk2del1/gprk2del2; (G,J) gprk2KO/gprk2del2.