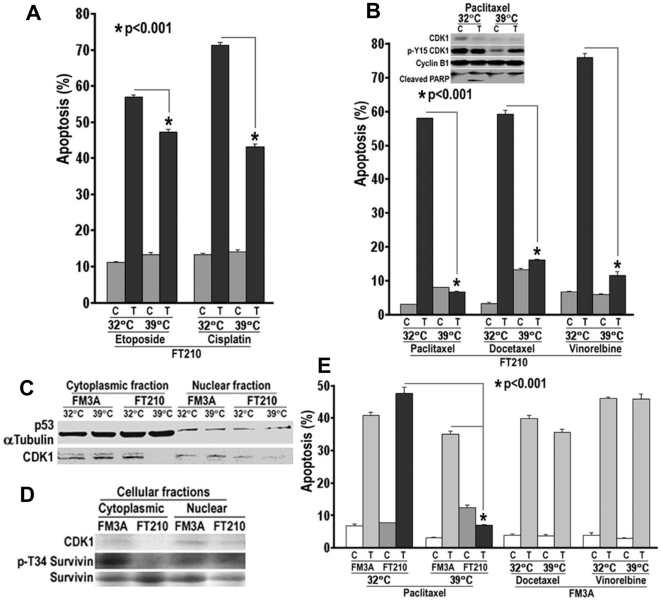
Figure 5. Loss of CDK1 protein and activity and chemotherapeutic resistance.
A. FT210 cells were serum-starvated in 0.1% FBS RPMI1640 medium overnight, then treated with 10 µM etoposide or cisplatin in 0.1% FBS containing medium for 4 days at 32°C or 39°C. Apoptosis (sub-G1 DNA content) was determined by flow cytometry (C: Control; T: Treatment). B. FT210 cells were cultured in normal medium and treated with 1 µM paclitaxel or docetaxel and 0.1 µM vinorelbine for 1–4 Days. The CDK1 protein was detected at Day 3 using CDK1 or p-Y15 CDK1 antibodies, and apoptotic death was monitored by PARP cleavage. Apoptosis was determined at Day 4. C. FT210 and its parental cell line FM3A cells were cultured for 6 h then subjected to subcellular fractionation for immunoblotting analysis. αTubulin and p53 served as loading controls for cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. D. FM3A and FT210 cells were cultured at 39°C for 72 h and subjected to subcellular fractionation. Expression of CDK1, p-Survivin (Thr34) and Survivin was assessed by immunoblotting. E. FM3A and FT210 cells were treated with 1 µM paclitaxel or docetaxel and 0.1 µM vinorelbine. Apoptosis was determined at Day 4.