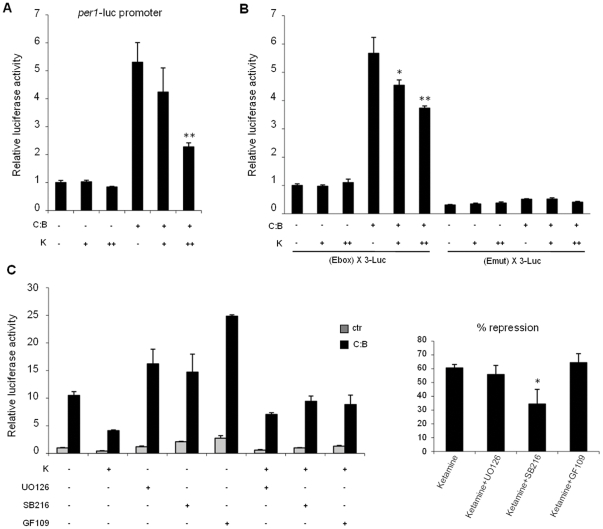
Figure 1. Ketamine treatment represses CLOCK:BMAL1 transactivation potential on the mPer1 gene promoter.
(A) Effect of ketamine on CLOCK:BMAL1 dependent transcription. Vectors expressing CLOCK:BMAL1 (C:B, 25 ng each) were cotransfected with a construct containing the mPer1 promoter (pGL3-mPer1-Luc, 50 ng) in NG108-15 cells. The total DNA amount was kept constant by adding carrier plasmid DNA. After 6 hs of transfection, cells were treated with increasing amounts of ketamine (K, 18 h, + as 10 mM and ++ as 1 mM). After normalization for transfection efficiency using β-galactosidase activity, reporter gene activities were expressed relative to those of a control transfected only with non-expressing plasmids. All the values are the mean +/− SD (n = 3); (**) p<0.01. (B) The E box promoter element mediates ketamine repression of CLOCK:BMAL1. Experimental conditions were as in A except that reporter constructs containing three copies of the E box consensus sequence (pGL3 promoter (E box) X3 LUC) or its mutated form (pGL3 promoter (Emut) X3 LUC) were used. All values are the mean +/− SD (n = 3); (*) p<0.05, (**) p<0.01. (C) Ketamine repression of CLOCK:BMAL1 involves activation of GSK3β. Experimental conditions were as in B except that the kinase inhibitors UO126 (ERK kinase inhibitor), SB216763 (GSK3β kinase inhibitor) and GF109203 (PKC kinase inhibitor) were applied to cells together with ketamine treatment (K, ++ as 1 mM). % of repression of CLOCK:BMAL1 transactivation with ketamine alone or ketamine with different kinase inhibitors is shown. All values are the mean +/− SD (n = 3); (*) p<0.05.