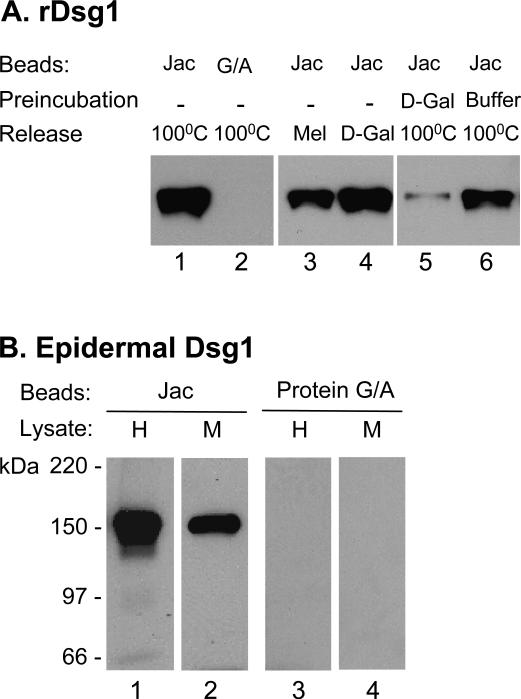
Figure 1. Jacalin binds Dsg1.
(A) Binding to rDsg1. rDsg1 was incubated with jacalin-agarose (lanes 1, 3-6) or protein G/A-agarose beads (lane 2). Bound-Dsg1 was released by boiling in SDS sample buffer (lanes 1-2 and 5-6) or eluted with jacalin-inhibiting sugars (lane 3: 0.1 M melibiose; lane 4: 0.8 M D-galactose). In one set of experiment, jacalin beads were preincubated with 0.8 M D-galactose (lane 5) or buffer (lane 6) before adding the PF serum to further show the sugar-dependency binding. Released Dsg1 was analyzed by IB using anti-His antibodies. (B) Binding to epidermal Dsg1. Tissue lysates from human (H) or mouse (M) epidermis were incubated with jacalin-agarose (lanes 1 and 2) or protein G/A-agarose beads (lanes 3 and 4) followed by IB using anti-Dsg1 antibodies.