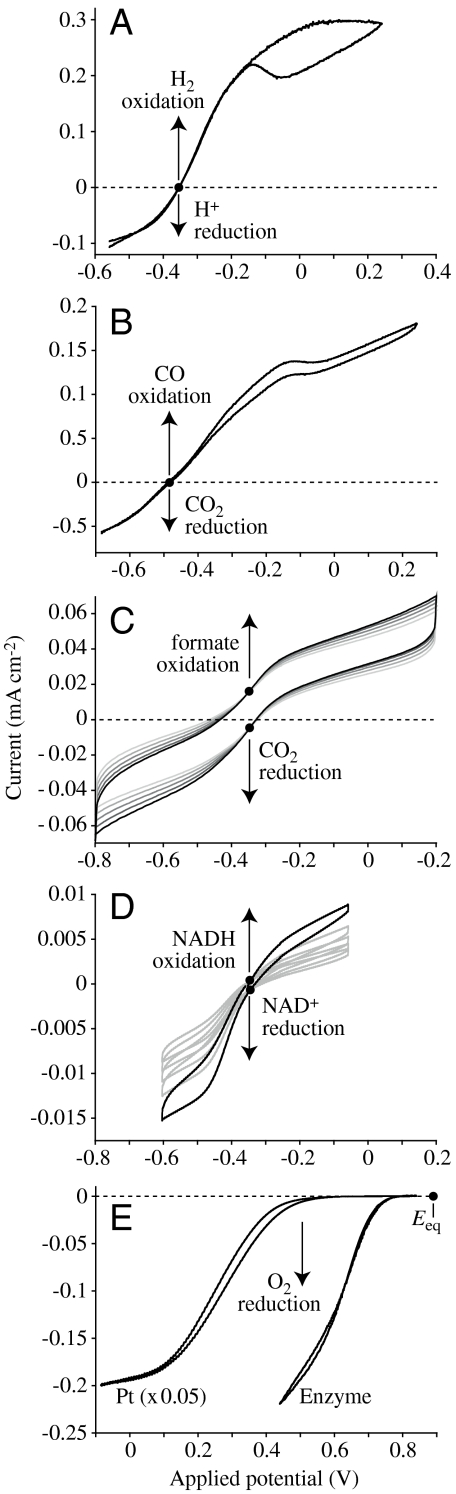
Fig. 2.
Direct electrocatalysis by enzymes visualized using cyclic voltammetry. All enzymes were adsorbed on rotating-disc pyrolytic graphite edge electrodes and both the oxidized and reduced substrates are present (in each case, • indicates Eeq, referenced to Standard Hydrogen Electrode). (A) Reversible interconversion of H+ and H2 by hydrogenase-2 from Escherichia coli (pH 6, 10% H2 in Ar, 30 °C; ref. 48). (B) Reversible interconversion of CO2 and CO by CODH 1 from C. hydrogenoformans (pH 7, 50% CO in CO2, 25 °C; ref. 17). (C) Reversible interconversion of CO2 and formate by FDH1 from S. fumaroxidans (pH 6.4, 10 mM carbonate, 10 mM formate, 37 °C; ref. 16). (D) Reversible interconversion of NADH and NAD+ by the hydrophilic domain of mitochondrial complex I (pH 7.8, 1 mM NADH, 1 mM NAD+, 20 °C; ref. 22). Multiple scans are included in C and D to aid identification of the zero-current points. (E) Irreversible reduction of O2 to H2O by either Pt(111), or by bilirubin oxidase from Myrothecium verrucaria (pH 5.8, 100% O2, 20 °C; ref. 27; the Pt(111) voltammogram has been decreased in size to faciliate comparison).