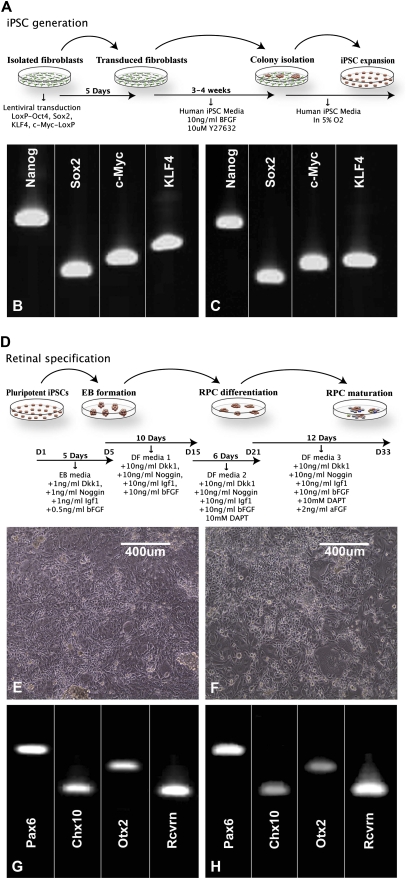
Fig. 3.
Production of retinal neurons from RP-control and RP-MAK iPSCs. (A) Schematic diagram illustrating the iPSC generation paradigm used in this study. (B and C) RT-PCR analysis of undifferentiated RP-control (B) and RP-MAK (C) iPSCs for expression of the iPSC/pluripotency markers Nanog, Sox2, c-Myc, and KLF4. (D) Schematic diagram illustrating the retinal differentiation paradigm used in this study. (E and F) Microscopic analysis of RP-control (E) and RP-MAK (F) iPSCs at 33 d postdifferentiation. (G and H) RT-PCR analysis of differentiated RP-control (G) and RP-MAK (H) iPSCs for the expression of the retinal specification/photoreceptor genes Pax6, Chx10, Otx2, and recoverin. At 33 d postdifferentiation, pluripotent iPSCs generated from both RP-control and RP-MAK human fibroblasts adopted a postmitotic retinal cell morphology and expressed the retinal specification/photoreceptor genes Pax6, Chx10, Otx2, and recoverin. (Scale bar: 400 μm.)