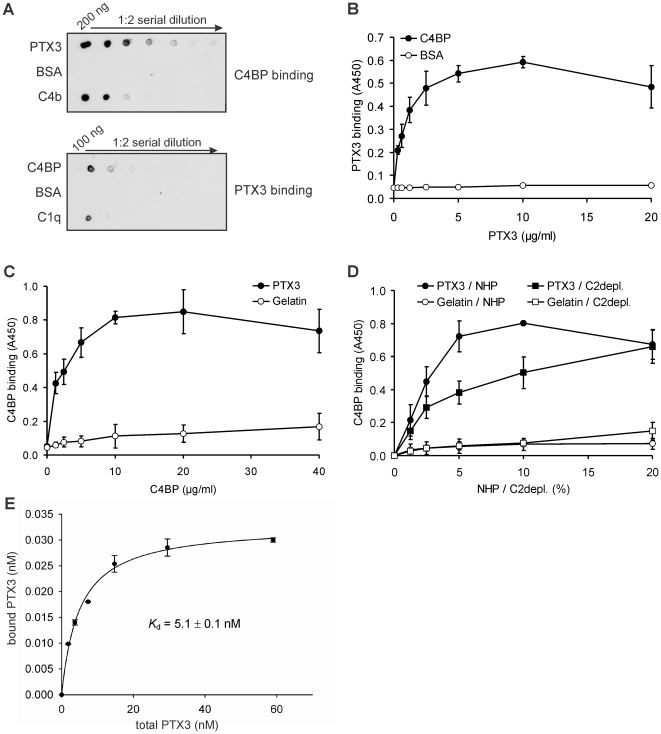
Figure 1. PTX3 interacts with the classical and lectin complement pathway regulator C4BP.
(A) Dot blot analysis of PTX3-C4BP interaction. Serial dilutions of PTX3, BSA and C4b were applied on a nitrocellulose membrane, and binding of 2 µg/ml C4BP was detected using a C4BP antiserum (upper panel). Serial dilutions of C4BP, BSA and C1q were applied on a separate membrane, and PTX3 binding (5 µg/ml) was detected using a polyclonal anti-PTX3 antibody (lower panel). The blots are representative of two and three experiments, respectively. (B) Dose-dependent binding of recombinant PTX3 to immobilized C4BP or BSA, used as negative control, was measured by ELISA. (C) In reverse experiments, binding of C4BP to immobilized PTX3 or gelatin, used as negative control, was analyzed. (D) Immobilized PTX3 (black symbols) or gelatin (white symbols) was incubated with the indicated concentrations of normal human plasma (NHP; circles) or C2-depleted serum (C2depl.; squares). Binding of native C4BP was detected using a C4BP antiserum. In B, C and D, the data are means ± SD derived from three experiments. (E) Addition of increasing amounts of PTX3 results in a saturable binding to immobilized C4BP. Specific binding was measured using a standard curve of PTX3, and the K d of 5.1±0.1 nM (mean ± SD from three experiments) was determined from non-linear regression analysis of the binding curve.