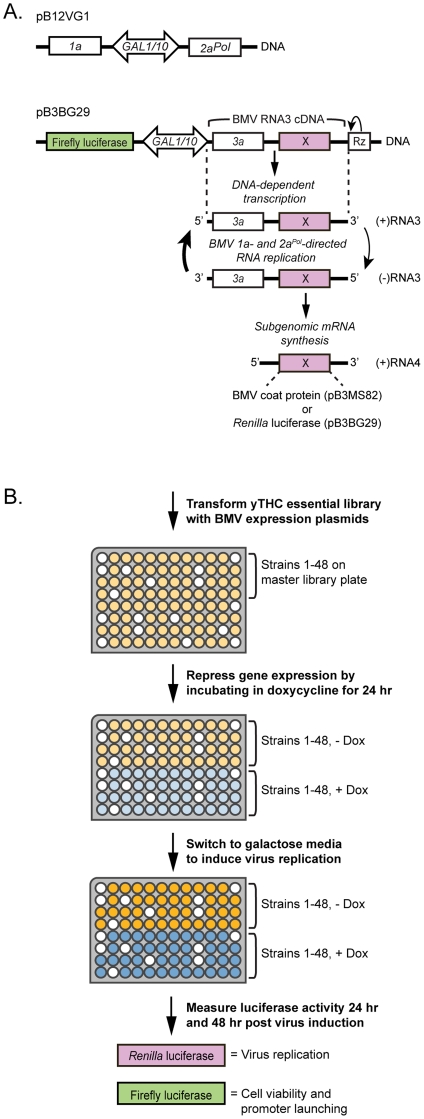
Figure 1. Yeast genetic screen used to identify essential host factors affecting BMV RNA replication.
(A) BMV expression plasmids. pB12VG1 expresses replication factors 1a and 2aPol. pB3BG29 expresses Fluc and RNA3. BMV-specific RNA-dependent RNA replication and subgenomic mRNA synthesis is initiated from a cDNA derivative of RNA3. DNA-dependent transcription produces an initial (+)RNA3 transcript that serves as a template for 1a- and 2aPol-dependent RNA3 replication and sgRNA4 synthesis via a (−)RNA3 intermediate. X, the BMV coat protein gene or any gene replacing it, such as Rluc (used here); GAL1/GAL10, yeast promoters, Rz, self-cleaving ribozyme. (B) 892 yeast strains, each with a single essential gene promoter replaced by a doxycycline (dox)-repressible promoter, were transformed with BMV expression plasmids. White wells indicate strains that did not transform. Transformants were re-formatted on 96-well plates with duplicates of each strain present on the same plate, allowing untreated and dox-treated strains to be directly compared. Strains were grown in raffinose-containing selective medium lacking dox (allowing essential gene expression) or containing 10 µg/ml dox (repressing essential gene expression) for 24 hr to allow for initial depletion of the essential gene mRNA and protein turnover in dox-treated strains. After this 24 hr treatment, strains were sub-cultured into galactose-containing selective medium ±10 µg/ml dox to induce expression of BMV components and subsequent viral RNA replication. Viral RNA replication was quantitated with a chemiluminescent Renilla luciferase assay at 24 hr and 48 hr post-virus induction. Cell viability and promoter launching were monitored with a chemiluminescent firefly luciferase assay at 24 hr and 48 hr post-virus induction. Two independent analyses of the library were performed.