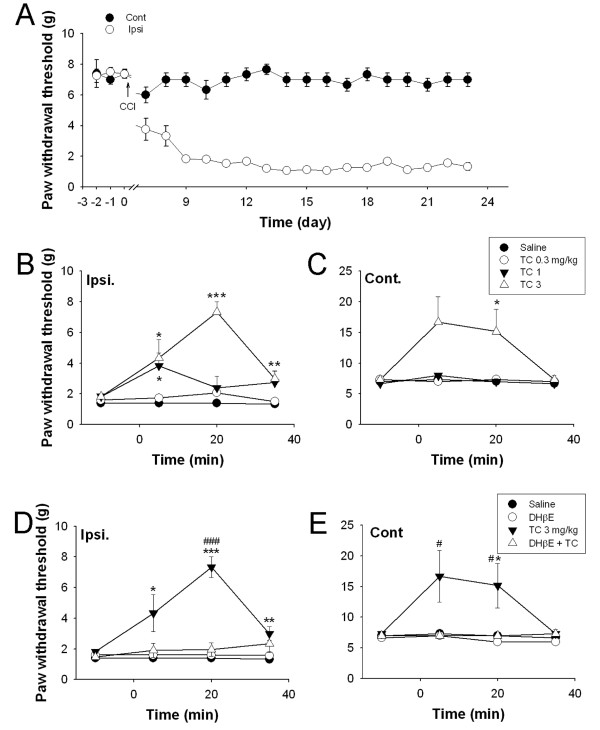
Figure 3.
TC-2559 dose dependently reduced CCI-induced neuropathic pain in rats. A, chart showing the progressive change of the paw withdraw threshold in both ipsilateral and contralateral hind paw before and after CCI injury. Note the enhanced mechanical allodynia in ipsilateral hind paw but not the contralateral uninjured hind paw. B-C, Traces showing TC-2559 (i.p.) dose dependently reversed CCI-induced mechanical allodynia in both ipsilateral (B) and contralateral (C) hind paws of CCI rats (n = 6 for each group). Note: at 1 mg/kg dose, TC-2559 only inhibited the mechanical allodynia in CCI hind paw (ipsilateral). D-E, Traces showing DHβE (2 mg/kg, i.p.) reversed TC-2559 (3 mg/kg, i.p.) induced mechanical allodynia inhibition in both ipsilateral and contralateral hind paws of the CCI rats (n = 6 for each group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared with saline. #P < 0.05 and ###P < 0.001 compared with 3 mg/kg TC-2559. (two-way ANOVA followed by the Holm-Sidak test).