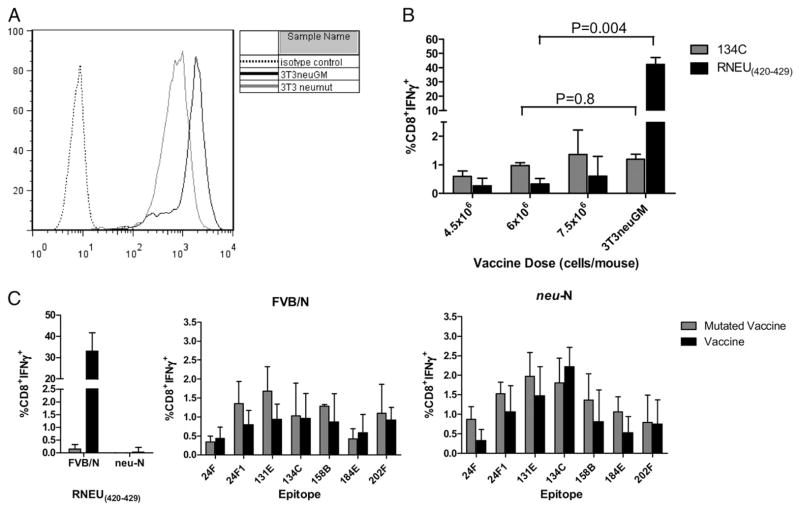
FIGURE 5.
Alanine substitution at anchor residue four within RNEU420–429 eliminates RNEU420–429-specific but maintains nondominant epitope-specific T cell responses following treatment of neu-N and FVB/N mice with the mutated vaccine. A, The 3T3neumut cell line expresses half the level of neu as 3T3neuGM vaccine cells. Full-length rat neu cDNA was mutated using PCR mutagenic primers and transfected into NIH-3T3 cells. Transfected cells were screened and sorted based on neu expression. B, Vaccination with 3T3neumut generates responses specific for 134C but not RNEU420–429. Three FVB/N mice were vaccinated with varying doses of 3T3neumut along with 3 × 106 3T3GM cells or 3 × 106 3T3neuGM cells. One week later, splenocytes were pulsed with either RNEU420–429 or the 134C epitope for 7 d. Lymphoctyes were isolated and incubated with T2-Dq cells pulsed with the corresponding peptide or NP118–126. Plotted is the mean percentage of CD8+ T cells that are IFN-γ + after subtraction of NP118–126 values. C, Nondominant CD8+ T cell responses are not significantly altered when comparing FVB/N and neu-N mice vaccinated with either the mutated or nonmutated vaccines. Experiments were carried out as described in B using 3 × 106 vaccine or 6 × 106 3T3neumut with 3 × 106 3T3GM cells. These experiments were repeated at least twice with similar results.