Fig. 4.
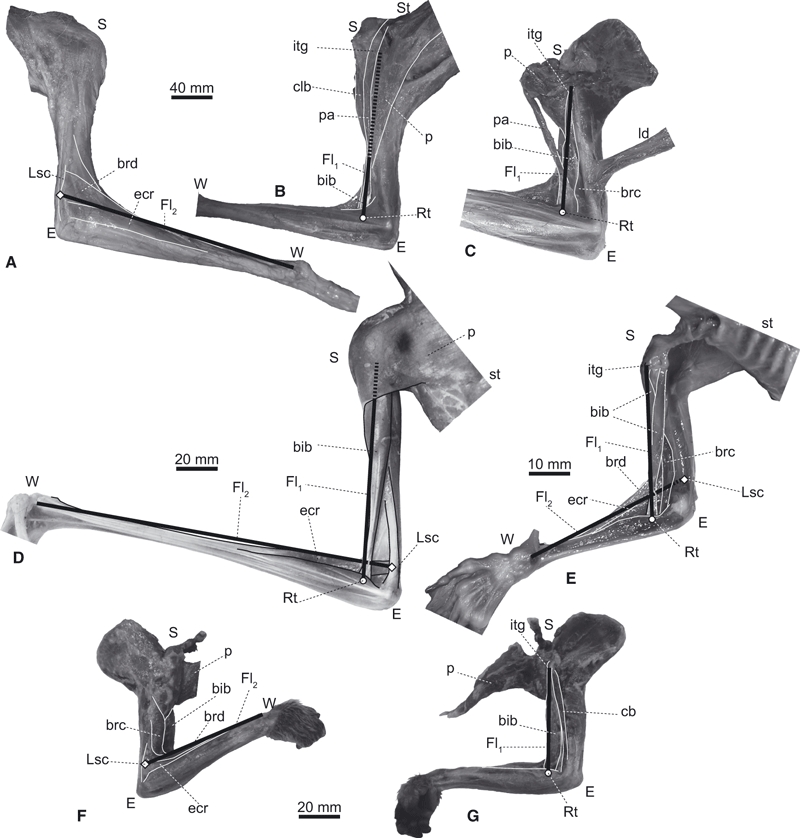
Elbow joint flexors of (A–C) Choloepus (UMUT unnumbered), (D) Pteropus (UMUT unnumbered), (E) Cynocephalus (ZRC 4.9464) and (F,G) Nycticebus (KPM 3684), in lateral (A,F) and medial views (B–E,G). Pectoral muscles are reflected or removed in C, E and G. A flexor muscle along the brachium (Fl1) is represented as a line connecting the inter-turbecular groove (itg) and the radial shaft (Rt). A flexor muscle along the antebrachium (Fl2) is represented as a line connecting the mid-portion of the lateral supracondylar crest (Lsc) and the wrist joint (W). bib, M. biceps brachii; brd, M. brachioradialis; cb, M. coracobrachialis; clb, M. cleidobrachialis; ecr, M. extensor carpi radialis; ld, M. latissimus dorsi; p, M. pectoralis; pa, part of M. pectoralis which inserts onto the antebrachium; st, sternum; E, S, and W, elbow, shoulder, and wrist joints, respectively. Note that our Fl1 and Fl2 groups best represent the paths of M. biceps brachii and M. extensor carpi radialis, respectively, but nonetheless are reasonable approximations of the paths, and thus moment arms, of the two major groups of elbow flexor muscles.
