Fig. 7.
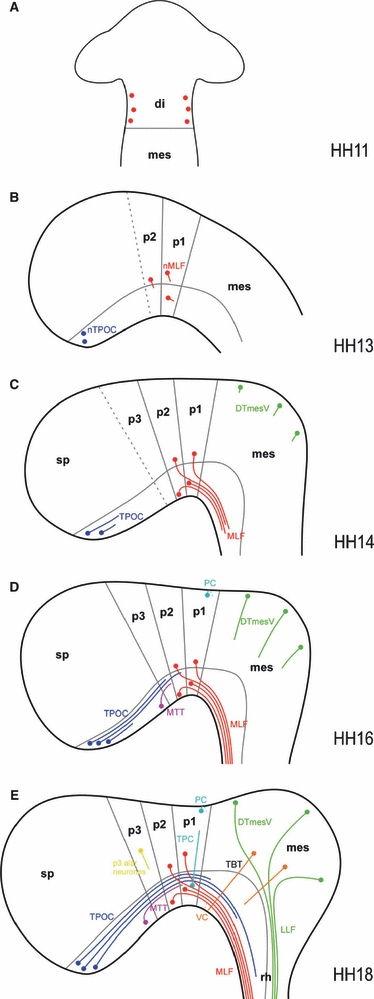
Developmental series of the chick early axon scaffold. Schematic representation of axon tract formation in the early embryonic chick brain. Neuromere boundaries (based on e.g. Larsen et al. 2001; Puelles & Rubenstein, 2003; Ferran et al. 2007) and the alar-basal plate border (reflecting the dorsal margin of Nkx2.2 expression and ventral margin of Pax3 expression) are shown in grey, while neurones and axons of the various early tracts are colour-coded (DTmesV, green; MLF, red; MTT, purple; PC/TPC, turquoise; TPOC, blue; VC, orange; dispersed alar p3 neurones, yellow). (A) HH11: the first MLF neurones appear within the diencephalon. (B) HH13: while the MLF neurones in the alar and basal pretectum begin to project axons, the TPOC neurones arise in the rostral basal hypothalamus. (C) HH14: in the pretectum, three populations of neurones contributing axons to the MLF in alar p1/p2, basal p1 and basal p2 are apparent. The MLF consists of a tight bundle of basal axons, close to the ventral midline. The TPOC axons have now started to project axons caudally through the secondary prosencephalon. The DTmesV neurones have appeared along the dorsal midline of the mesencephalon and start to project axons ventrally. (D) HH16: the TPOC axons have reached the MLF in p1. Located in between the TPOC and MLF neurones, the MTT neurones have arisen in the basal plate of the caudal secondary prosencephalon. These axons initially follow the TPOC axons to join the VLT. Neurones at the dorsal midline of p1 project axons contralaterally to pioneer the PC. (E) HH18: the principal tracts of the chick early axon scaffold have formed. In the pretectum, TPC neurones have appeared in ventral p1 and project axons dorsally along the DMB, while in the mesencephalon tectobulbar neurones project their axons ventrally. di, diencephalon; DTmesV, descending tract of the mesencephalic nucleus of the trigeminal nerve; LLF, lateral longitudinal fascicle; mes, mesencephalon; MLF, medial longitudinal fascicle; MTT, mamillo-tegmental tract; p1, prosomere 1/pretectum; p2, prosomere 2/thalamus; p3, prosomere 3/prethalamus; PC, posterior commissure; rh, rhombencephalon; sp, secondary prosencephalon; TBT, tectobulbar tract; TPC, tract of the posterior commissure; TPOC, tract of the postoptic commissure; VC, ventral commissure.
