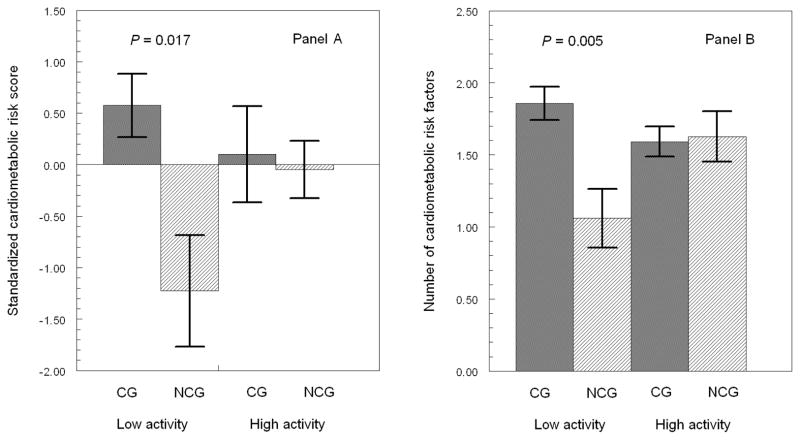
Figure 1. Regular Physical Activity and Cardiometabolic Risk Indices.
Error bar graphs (mean±SEM) show significantly greater standardized cardiometabolic risk score (A) and also greater number of cardiometabolic risk factors (B) in 115 caregivers (CG) and 54 non-caregivers (NCG) with the same level of low physical activity; CG and NCG with the same level of high physical activity have similar cardiometabolic risk indices. All analyses controlled for gender, age, education, smoking, alcohol consumption, health problems, cholesterol-lowering medication, negative affect, role overload, and fasting state.