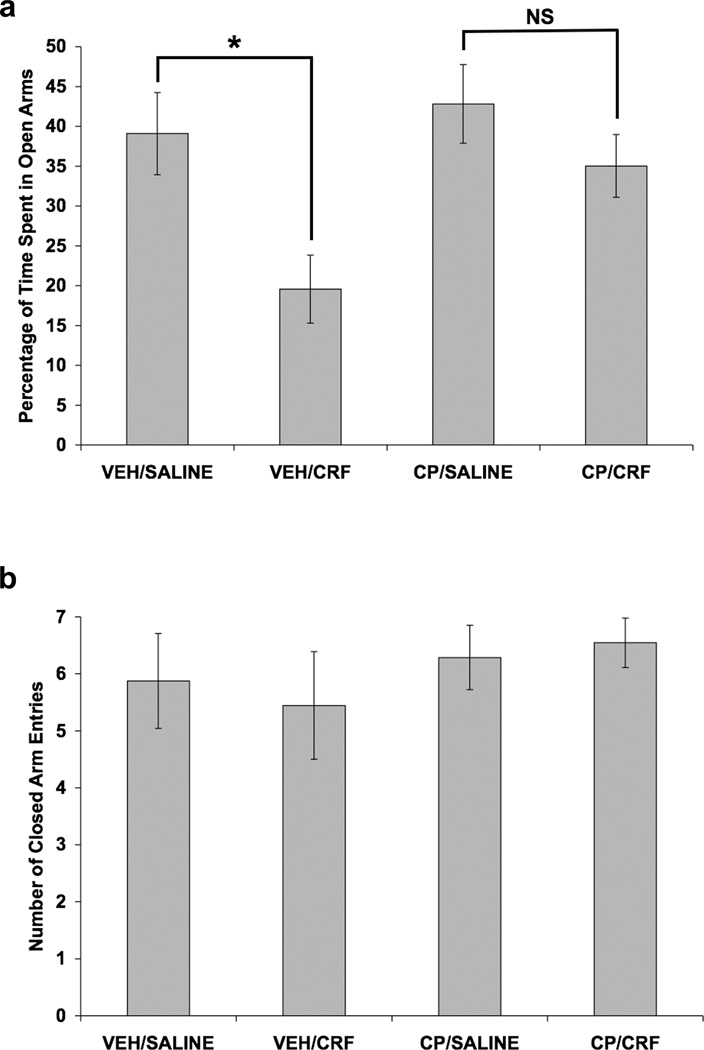
Fig. 7.
Effect of CRF and selective CRF1 receptor blockade on anxiety-like behavior in the elevated plus maze. Values shown are mean ± SEMs. For all groups, n = 7–11. X-axis shows Pretreatment (SC injection)/Treatment (ICV infusion). Rats received a SC injection of CP-154,526 (20.0 mg/kg) or vehicle. Two hours and forty-five minutes later, rats received an ICV infusion of 1.0 µg CRF (in 5.0 µl saline) or 5.0 µl saline. Ten minutes after ICV infusion, rats were observed in the elevated plus maze for 5 minutes. (a) CRF infusion decreased the percentage of time spent in the open arms of the maze only in vehicle-pretreated rats (*p = 0.010, independent t-test comparing VEH/SALINE to VEH/CRF). Since CP/SALINE and CP/CRF groups did not differ significantly (NS), CP-154,526 pretreatment blocked the CRF-induced increase in anxiety-like behavior in the elevated plus maze. (b) Neither CP-154,526 injection nor CRF infusion altered the number of closed arm entries.