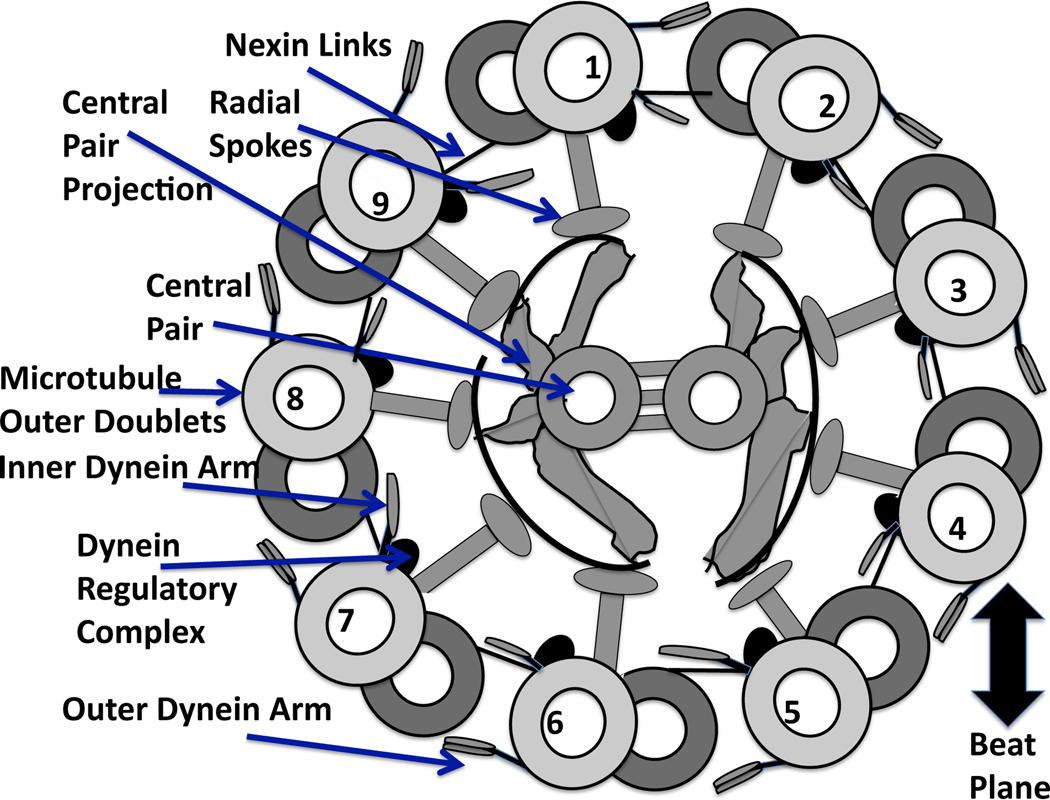
Fig. 1.
Diagram of a cross section of the “9+2” axoneme, recreated from [93], and viewed from base toward tip. Each of the internal structures of the flagellum are labeled with arrows. The central pair are positioned perpendicular to the beat plane, which is defined by dyneins on doublets 1–4 bending the axoneme in one direction, followed by the deactivation of these dyneins and the activation of the opposite group of dyneins on doublets 6–9 [14, 56].