Figure 1. FV vectors.
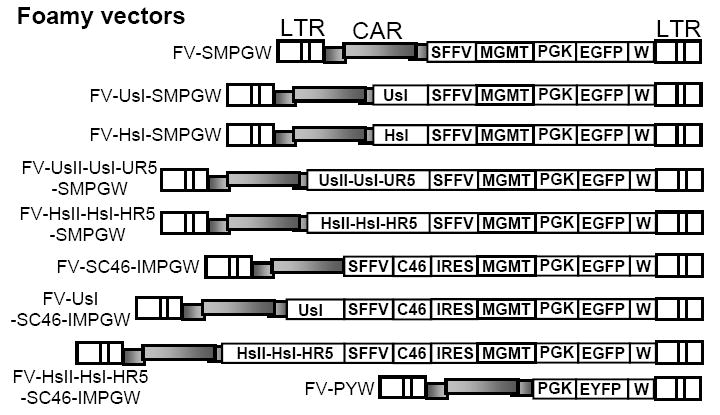
The FV vector FV-SMPGW contains an SFFV promoter (S) driving expression of the P140K mutant of MGMT (M) and also contains a human PGK promoter (P) driving expression of EGFP (G). This vector also contains a safety modified WPRE element (W). The following anti-HIV transgenes were added to this vector; a human U6 Pol III promoter that expresses an shRNA targeted to tat/rev at site I (FV-UsI-SMPGW), a human H1 Pol III promoter driven shRNA targeted to tat/rev at site I (FV-HsI-SMPGW), a combinatorial cassette with H1 promoter driving shRNAs targeted to tat/rev at site I and site II and to human CCR5 at bp 1023 (FV-HsIHsIIHR5-SMPGW). A combinatorial cassette with the U6 promoter driving shRNAs targeted to tat/rev at site I and site II and to human CCR5 at bp 741 (FV-UsIUsIIHR5-SMPGW), the transmembrane-localized C46 HIV envelope fusion inhibitor expressed from the SFFV promoter with an IRES expressing MGMT (FV-SC46-IMPGW), the U6 driven tat/rev site I shRNA combined with the C46-expressing vector (FV-U6sI-SC46-IMPGW) and the combinatorial H1 driven cassette with shRNAs targeted to tat/rev at site I and site II and to human CCR5 at bp 1023 combined with the C46-expressing vector (FV-HsII-HsI-HR5-SC46-IMPGW). The control FV vector FV-PYW has the human PGK promoter driving EYFP (Y). The long terminal repeats (LTR) and foamy cis-acting region (CAR) are also indicated.
