FIGURE 4.
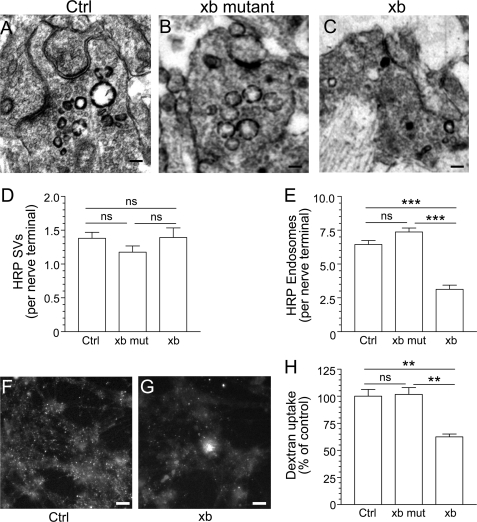
The CaN-dynIxb interaction is essential for ADBE. Cerebellar granule neuron cultures were incubated with 10 mg/ml HRP, and loading was stimulated by a train of 800 action potentials delivered at 80 Hz. The cultures were incubated with either wild-type (xb) or mutant containing ARATA (xb mut) penetratin-tagged peptide dynIxb(842–851) (60 μm) for 15 min before and during stimulation. A–C, HRP-labeled structures in typical fields of view either in the absence of peptide (A, Ctrl) or in the presence of mutant (B) or wild-type peptide (C). Scale bar, 150 nm in all images. D, mean number of HRP-labeled SVs generated per nerve terminal in the presence of the peptide. E, mean number of HRP-labeled endosomes generated per nerve terminal in the presence the peptide. Data were pooled from either four (Ctrl) or three (xb mut and xb) independent experiments (Ctrl, n = 173 nerve terminals; xb mut, n = 119; xb, n = 87; all mean ± S.E.; ***, p < 0.001 compared with control, one-way analysis of variance; ns, not significantly different). F and G, dextran loading in typical fields of view in cerebellar granule neurons either in the absence of xb peptide (F) or in its presence (G). Scale bars (F and G), 15 μm. H, granule neurons were incubated with 50 μm tetramethyrhodamine-dextran and loading was stimulated by a train of 800 action potentials (80 Hz) followed by immediate dextran washout. Where indicated, cultures were incubated with 60 μm either wild-type or mutant xb peptide 15 min before and during stimulation. The data shown are mean number of dextran puncta per field of view as a percentage of control (n = 4 ± S.E.; **, p < 0.01, one-way analysis of variance).