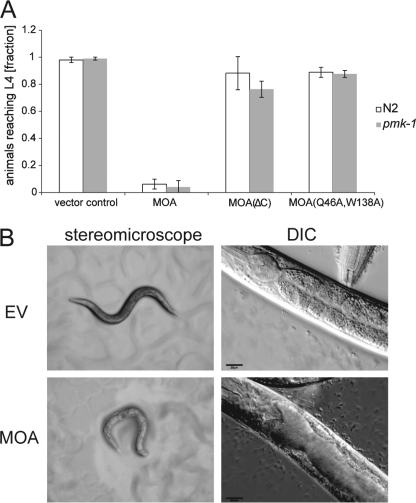
FIGURE 1.
Recombinant MOA displays carbohydrate binding-dependent toxicity toward C. elegans. E. coli BL21(DE3) cells expressing MOA, the C-terminal deletion mutant MOA(ΔC), or the carbohydrate binding-deficient variant MOA(Q46A,W138A) or containing an empty vector were fed to C. elegans N2 wild-type and pmk-1(km25) mutant worms. A, MOA inhibits C. elegans development. The fraction of C. elegans L1 larvae having developed to the L4 stage was scored after 72 h of feeding on a lawn of respective E. coli BL21 cells. Bars represent the average of nine biological replicates. Error bars indicate S.D. B, MOA damages the C. elegans intestine. C. elegans N2 wild-type L4 larvae were fed MOA-expressing (lower panels) and control, i.e., empty-vector (EV) containing (upper panels) E. coli BL21(DE3) cells and examined after 24 h under a stereomicroscope (left panels) and by differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy (right panels). Scales bars = 20 μm.