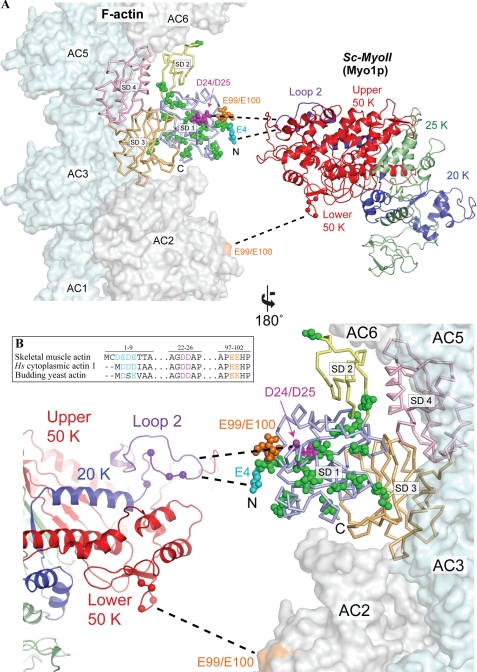
FIGURE 1.
Actin mutations at the predicted actomyosin interface. A, structural model depicting the predicted binding interface between yeast actin and myosin-II. Yeast actin (Act1p, 1YAG) (41) was superimposed onto one of the actin momomers (AC4) in the actomyosin model of Holmes et al. (42). Actin subdomains 1–4 (SD1-SD4) are colored separately. A three-dimensional structure of the yeast myosin-II Myo1p (Sc-MyoII) motor was predicted using the I-TASSER protein structure and function prediction server (43), and colored to indicate the 50K domain (red), 25K domain (green) and 20K domain (blue). The Sc-MyoII motor was superimposed onto the skeletal muscle myosin structure (2MYS) (44) in the orientation predicted for the actomyosin complex, but separated horizontally to expose the binding interface. The cationic loop 2 of Sc-MyoII is indicated in purple. Mutations concentrated in subdomain 1 of the outer domain are shown in space-filling representation for the actin monomer set within the actin filament. Residues relating to the 4Ac (cyan), sub12 (green), D24A-D25A (pink), and E99A-E100A (orange) mutants are shown. For 4Ac actin, of the four glutamates located at the N terminus in this mutant form, only the E4 residue is shown. The sixteen mutations in sub12 are as follows: V5T, A6T, I10C, M16L, C17V, I43V, R68K, V76I, V103T, M110L, S114A, F132M, S135A, T350S, S358T, and H372R. Dashed lines indicate proposed myosin binding sites (which span two adjacent actin monomers): loop 2 to 4Ac, D24-D25 (primary binding site); lower 50K loop to E99-E100 (secondary binding site). The position of positively charged residues within these two Sc-MyoII loops are indicated (balls). B, amino acid sequence homology centered on the negatively charged N termini and D24-D25/E99-E100 amino acid pairs of human skeletal muscle actin, human cytoplasmic actin-1, and budding yeast actin. Alignments were generated using the ClustalX software (45).