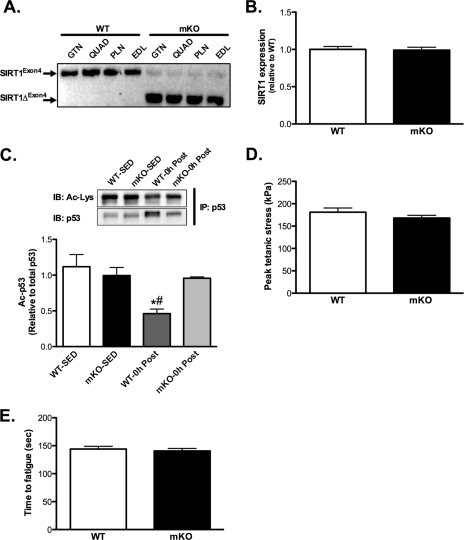
FIGURE 1.
Loss of SIRT1 activity does not affect skeletal muscle contractile characteristics. A, semiquantitative PCR analysis using primers directed across exon4 of the SIRT1 gene in skeletal muscle (gastrocnemius (GTN), quadriceps (QUAD), plantaris (PLN), and extensor digitorum longus (EDL)) of WT and mKO mice. Note the shorter PCR product in mKO mice (SIRT1ΔFLX-Exon4), indicating efficient deletion of exon4. B, deletion of exon4 does not affect SIRT1 gene expression in gastrocnemius muscle. C, deacetylation of p53 occurs after AEX (0 h after) in gastrocnemius muscle from WT but not mKO mice, compared with SED mice. D and E, maximal tetanic force (D) and time to fatigue (E) in isolated fifth toe of the extensor digitorum longus muscle of WT and mKO mice. All data are presented as mean ± S.E. (error bars). #, within 0h; *, within genotype p < 0.05.