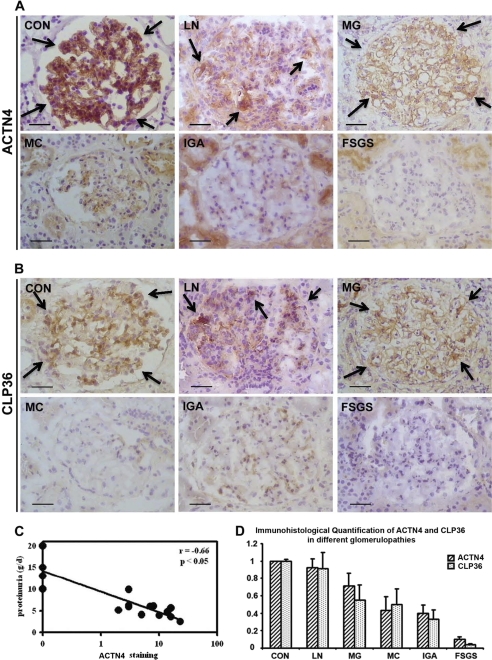
FIGURE 1.
Deficiencies of α-actinin-4 and CLP36 in human glomerulopathies. A and B, immunohistochemical staining of α-actinin-4 (A) and CLP36 (B) in human glomeruli. Arrows in CON, LN, and MG indicate some of the representative areas of α-actinin-4 and CLP36 staining (brown color). Scale bars, 50 μm. C, correlation of proteinuria and the reduction of the α-actinin-4 level in FSGS. Proteinuria determined in 24-h urine samples correlated negatively with α-actinin-4 staining (n = 16) in human FSGS patients. D, close correlation of the levels of α-actinin-4 and CLP36 in human glomerulopathies. The levels of α-actinin-4 and CLP36 were quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Note that the extent of the reduction of CLP36 correlated closely with that of α-actinin-4 in glomerulopathies. CON, control kidney; LN, lupus nephritis; MG, membranous glomerulopathy; MC, minimal change disease; IgA, IgA nephropathy. Error bars, S.D.