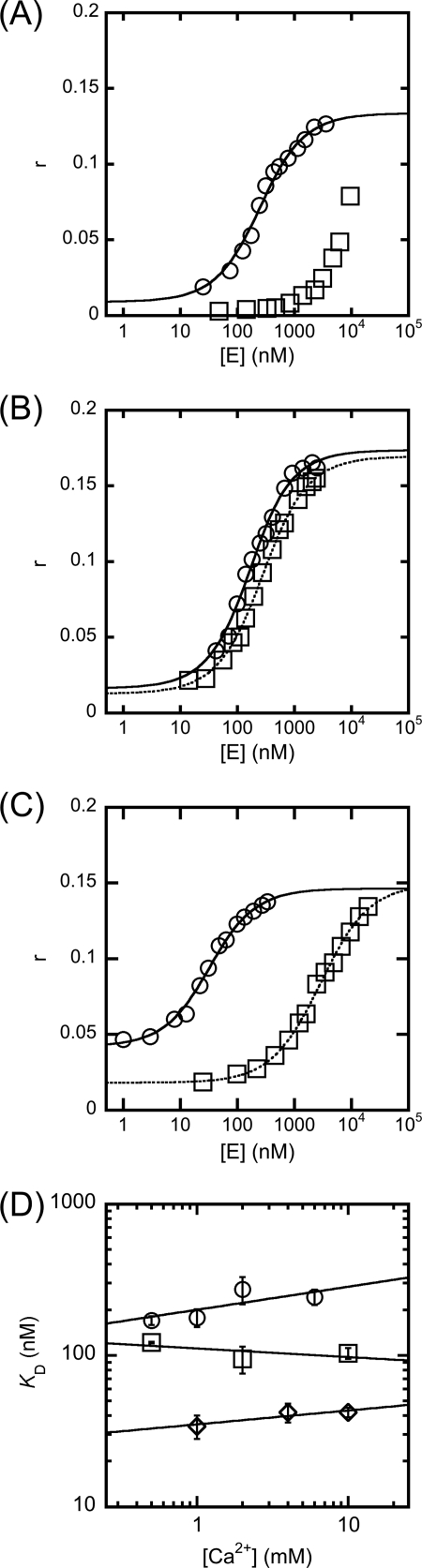
FIGURE 2.
The effects of calcium ions on WT and D210I/D204S FEN-substrate dissociation constants evaluated by fluorescence anisotropy (r). Experimental details are contained under “Experimental Procedures,” and all experiments were carried out in triplicate. Constant ionic strength of potassium and calcium ions was maintained by varying the amount of KCl present. A, the addition of WT T5FEN to 100 nm HP5F at pH 9.3, in the presence of 2 mm EDTA (squares) and 1 mm Ca2+ ions (circles). Curve fitting to Equation 1 yields KD = 202 ± 27 nm (1 mm Ca2+). Without divalent metal ions present, the binding curve did not reach saturation. B, the addition of WT T5FEN to 100 nm HP5F at pH 7.5, in the presence of 2 mm EDTA (squares) and 1 mm Ca2+ ions (circles). Curve fitting to Equation 1 yields KD = 231 ± 13 nm (no divalent ion) and KD = 120 ± 13 nm (1 mm Ca2+). C, the addition of D210I/D204S T5FEN to 10 nm HP5F at pH 9.3, in the presence of 2 mm EDTA (squares) and 0.5 mm Ca2+ ions (circles). Curve fitting to Equation 1 yields KD = 2880 ± 160 nm (no divalent ion) and KD = 28 ± 3 nm (0.5 mm Ca2+). D, variation of log KD as a function of log [Ca2+] for WT T5FEN at pH 9.3 (circles), pH 7.5 (squares), and D210I/D204S T5FEN at pH 9.3 (diamonds). The slopes of the resultant plots are 0.15 ± 0.10, −0.06 ± 0.06, and 0.09 ± 0.04, respectively. Error bars indicate S.E.