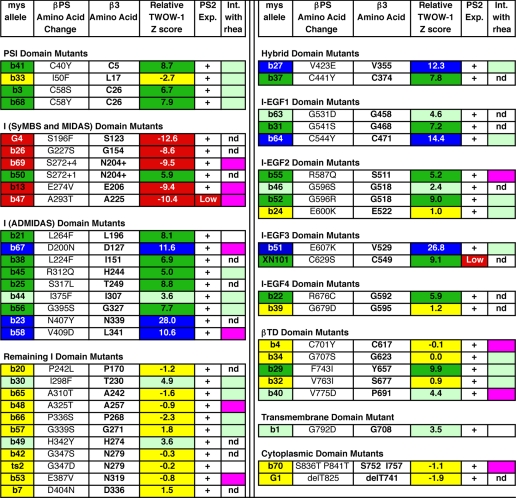
TABLE 1.
Summary of mys mutant TWOW-1 binding, expression, and genetic interactions with rhea
This is a summary of the detailed data that can be found in supplemental Tables S1–S3 and S5. Mutants are grouped by domains. Color coding of the mys allele and TWOW-1 z score boxes is the same as in Fig. 1: red, very low affinities for TWOW- 1 (z scores <−8); yellow, wild type affinities (z scores between −3 and 3); light green, moderately elevated affinities (z scores between 3 and 5); dark green, very elevated affinities (z scores between 5 and 10); blue, extremely elevated affinities (z scores >10). The one exception to this color coding is mysb46. Its p value was significant (<0.001), so it was shaded light green, although its z score was only 2.4. For mysb69 and mysb50, S272+4 and S272+1 indicate insertions of VRQ or Q following amino acid 272. For mysG1, de1T825 refers to the carboxyl-terminal 21 amino acids deleted and replaced by 25 essentially random amino acids (due to a splice site mutation). mysb24 is a mutation of the single amino acid between I-EGF2 and I-EGF3. (For convenience, it has been placed in the I-EGF2 group). For the genetic interaction tests with rhea (Int. with rhea), magenta indicates an enhancing interaction; flies with the βPS mutation are more lethal with only one wild type copy of rhea than when they contain two wild type copies of rhea. Light green indicates a rescuing interaction; flies with the βPS mutation are less lethal with only one wild type copy of rhea than when they contain two wild type copies of rhea. No shading indicates a lack of significant difference in lethality. In some cases, the interaction test was not done (nd) due to too much or too little lethality of the mys allele.