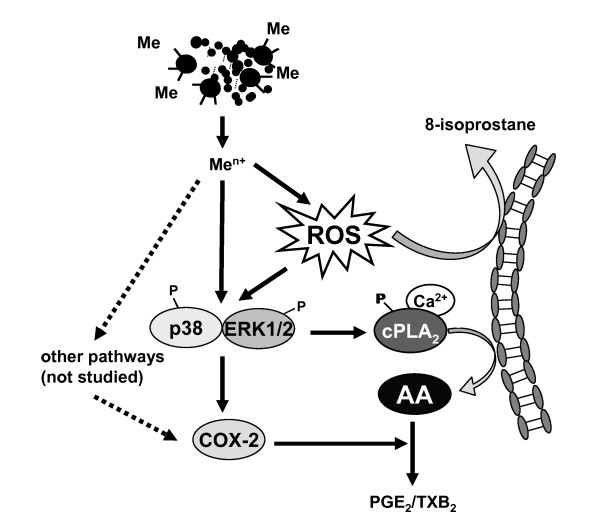
Figure 9.
Scheme of the MAF02-induced activation of the arachidonic acid cascade. The MAF02 particles are taken up by RAW264.7 macrophages and release metal ions (Men+) inside the cells which induces formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Release of 8-isoprostane indicates the occurrence of oxidative stress. Oxidative stress in turn leads to activation of the ERK1/2 and p38 pathways. The ERK1/2 pathway may be activated by interfering of the particles with membrane proteins. On the other hand, enhanced MAPK activation can also occur by inhibition of metal- and redox-sensitive phosphatases, which dephosphorylate and inactivate MAPK. Activation of ERK1/2 and p38 leads to phosphorylation and activation of cPLA2 (cytosolic phospholipase A2). The increase of the intracellular calcium level induces cPLA2 translocation to the perinuclear membranes where it catalyzes the mobilization of AA. On the other hand, it is possible that ROS inhibit the reacylation of AA, which would also lead to an enhanced level of free AA in the cytosol. Free AA is converted by COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) and prostaglandin synthases to PGE2/TXB2 (prostaglandin E2/thromboxane B2). Increased transcription of COX-2 requires activation of ERK1/2 and p38, but may also involve other pathways e.g. NF-κB.