Figure 2.
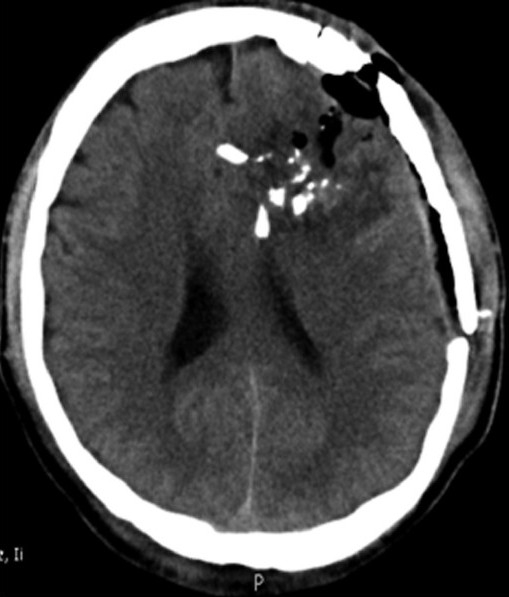
The computed tomography (CT) scan of brain showing left frontal penetrating injury causing multiple fractures and pneumocranium. Multiple bone fragments are displaced within brain parenchyma resulting in contusion and edema. This male patient, a blast victim, at presentation was localizing to pain and had right hemiparesis. He underwent craniotomy, debridement, including removal of superficial intracranial bone fragments, wound refashioning, and primary closure. Post - operative course was unremarkable and at 6 months follow - up, the patient was completely independent, although he had persistent mild hemiparesis
