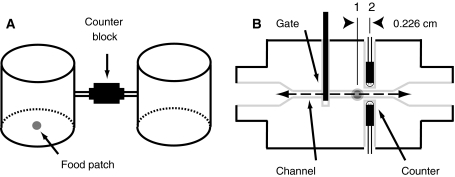
Fig. 1.
Instrument devised to study the movement of Drosophila between controlled sensory environments. a Illustration showing two experimental chambers connected by tubes feeding into the opposite sides of a counter block. For dispersal experiments, we either did or did not provide a patch of food in the middle of the chamber floor. b Schematic of a gate and bi-directional counting block. We drove each gate with a solenoid (push-pull type) motor and monitored the transition of flies through a channel within the counting blocks with two pairs of infrared emitter/detector diodes, denoted as 1 and 2. Note that the second pair of diodes is offset from the first pair by 0.226 cm (measured between diode centers) and are not shown in the drawing. The second set of diodes would project normal to the plane of the drawing (gray dot)