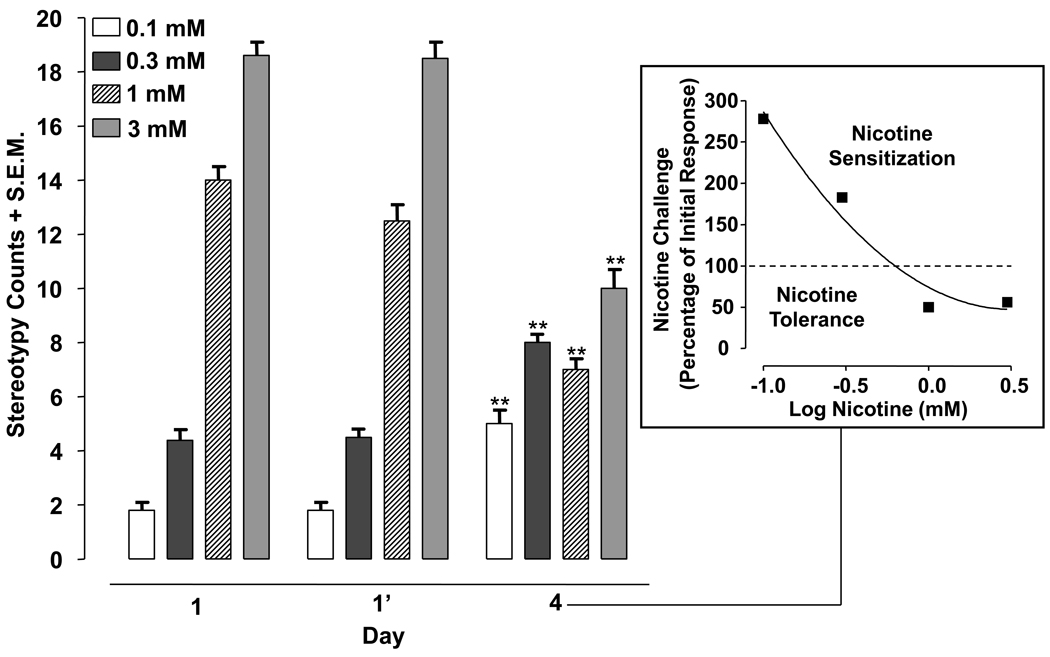
Fig. 3.
Low concentrations of nicotine produce sensitization of stereotypical activity and high concentrations of nicotine produce tolerance to stereotypical activity. Planarians were exposed to nicotine (0.1, 0.3, 1, 3 mM) twice on day 1 (120 min apart) and then re-exposed to the same concentration of nicotine for 5 min on day 4. Data are expressed as mean stereotypy counts + S.E.M. during 5 min of nicotine exposure versus day (1, 1’, 4). **p < 0.01 compared to the stereotypy counts produced by initial drug exposure (day 1). N = 8 planarians per group. Box) The percentage of the initial nicotine response (day 1) produced by nicotine challenge on day 4 is plotted versus log nicotine concentration.