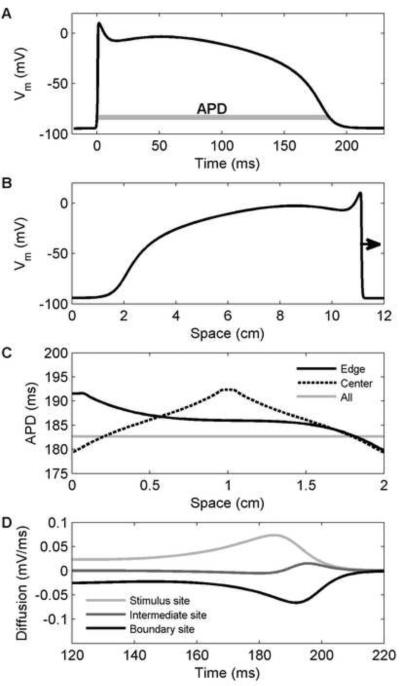
Figure 1.
Action potential properties of the Fox-McHarg-Gilmour (FMG) model [24] in a one-dimensional cable. A. Action potential from the center of a cable 2 cm long stimulated at one end. Action potential duration (APD) is indicated. B. Profile of a wave propagating from left to right 220 ms after initiation at the left edge. A long cable (12 cm) was used to fit an entire wavelength. C. Spatial distribution of APD along the cable for a stimulus at the left edge (solid), at the center (dashed), or everywhere (gray) to eliminate the effects of coupling. D. Diffusion currents during repolarization for center stimulus case of panel C at locations within the stimulated region (light gray), at the boundary (black), and halfway between (dark gray). Within the stimulated region, the current is large and positive, which lengthens APD. At the boundary, the current is large and negative, which shortens APD.