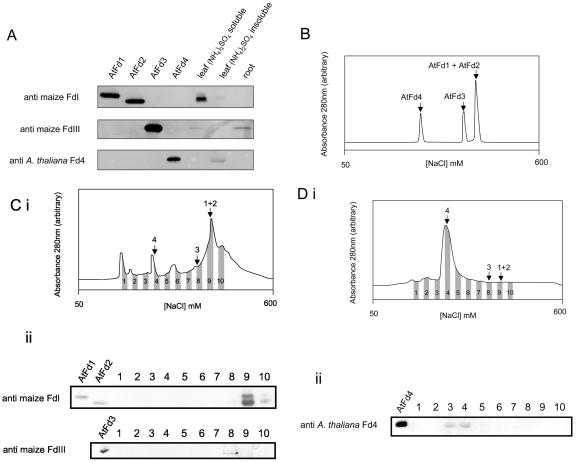
Figure 5.
Detection of AtFd proteins in planta. A, Western blots using antibodies specifically reacting with leaf type Fds (raised against maize FdI), root type Fds (raised against maize FdIII), and AtFd4 (raised against AtFd4). Control lanes were loaded with 200 nmol of recombinant proteins, except for detection by anti-AtFd4, where 20 nmol of AtFd4 was used. Mature Arabidopsis leaf proteins were separated into fractions soluble and insoluble in 70% saturated (NH4)2SO4, and gels were loaded with the equivalent to 12 μg of total leaf protein, except when detecting with anti-AtFd4, where 90 μg was used. Twenty micrograms of Arabidopsis root protein was loaded. B, Elution profiles of recombinant AtFd1, AtFd2, AtFd3, and AtFd4 from an anion exchange column, over a salt gradient (based on conductivity of the eluent). C, i, Elution profile of Arabidopsis leaf proteins soluble in 70% saturated (NH4)2SO4. Arrows indicate relative elution positions of recombinant proteins: 1 + 2, AtFd1 and AtFd2; 3, AtFd3; 4, AtFD4. ii, Western blots to detect putative AtFd1 and AtFd2 after SDS-PAGE (top) and putative AtFd3 after gradient native PAGE (bottom). Two hundred nanograms of recombinant proteins was used as controls. D, i, Elution of Arabidopsis leaf proteins insoluble in 70% saturated (NH4)2SO4. Arrows as described above. ii, Labeled fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE and challenged with anti-AtFd in the western blot displayed. Twenty nanograms of recombinant AtFd4 was used as a control. All western blots are representative of two to three separate experiments.