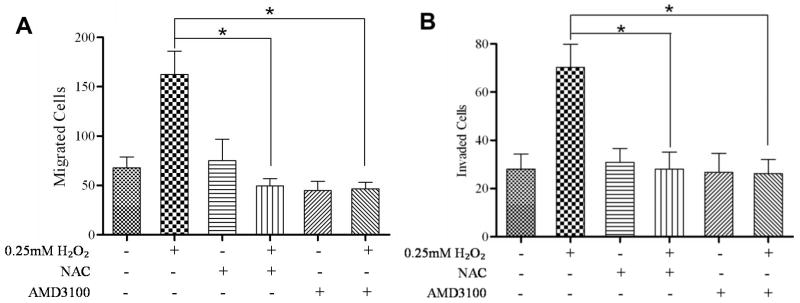
Figure 3. ROS enhanced migration and invasion in a CXCR4-dependent manner.
Migration assays: 4×104 cells each were seeded into the upper transwell chamber and allowed to migrate towards various treatments in the lower chanber for 6 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2. Five fields of each transwell insert were randomly selected and counted for migrated cells at 10× magnification using a Zeiss Axiovert 200M light microscope and graphed. (A) A graphical representation of total migrated cells. Experiments were repeated thrice, and data represents the averages of 3 independent experiments. Invasion assays: 8×104 cells each were seeded into the upper transwell chamber layered with matrigel and allowed to invade towards the indicated treatments in the lower chamber for 24 hours at 37°C, 5% CO2. Five fields of each transwell insert were randomly selected and counted for invaded cells at 10× magnification using a Zeiss Axiovert 200M light microscope. (B) A graphical representation of total invaded cells. Experiments were repeated thrice, and data represents the averages of 3 independent experiments. *, P < 0.05.