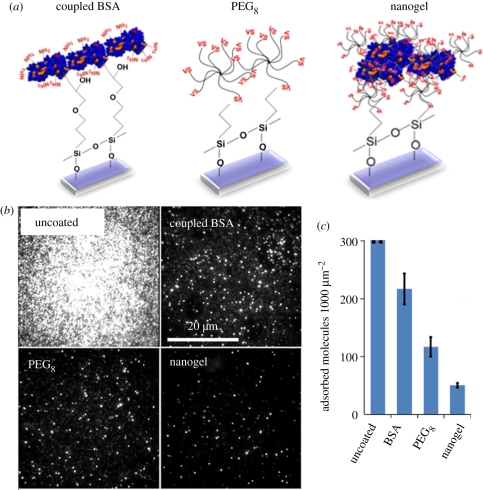
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of three coating methodologies: bovine serum albumin (BSA) covalently coupled to epoxysilanated glass, multi-arm PEG (PEG8) coupled to mercaptosilanated glass and PEG–BSA nanogels coupled to mercaptosilanated glass. (b) Antibody adsorption onto uncoated, BSA-coated, multi-arm PEG-coated and PEG–BSA nanogel-coated surfaces was quantified by total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) imaging, and representative raw TIRF images are shown. (c) Molecule counts of antibody adsorption per unit area. On the uncoated surface, molecular density was so high that single-molecule counting was not possible. BSA-coated, multi-arm PEG-coated and nanogel-coated surfaces show decreased antibody adsorption compared to the uncoated surfaces, with the nanogel-coated surface performing the best. Error bars represent standard deviation of triplicate substrates.