Figure 4.
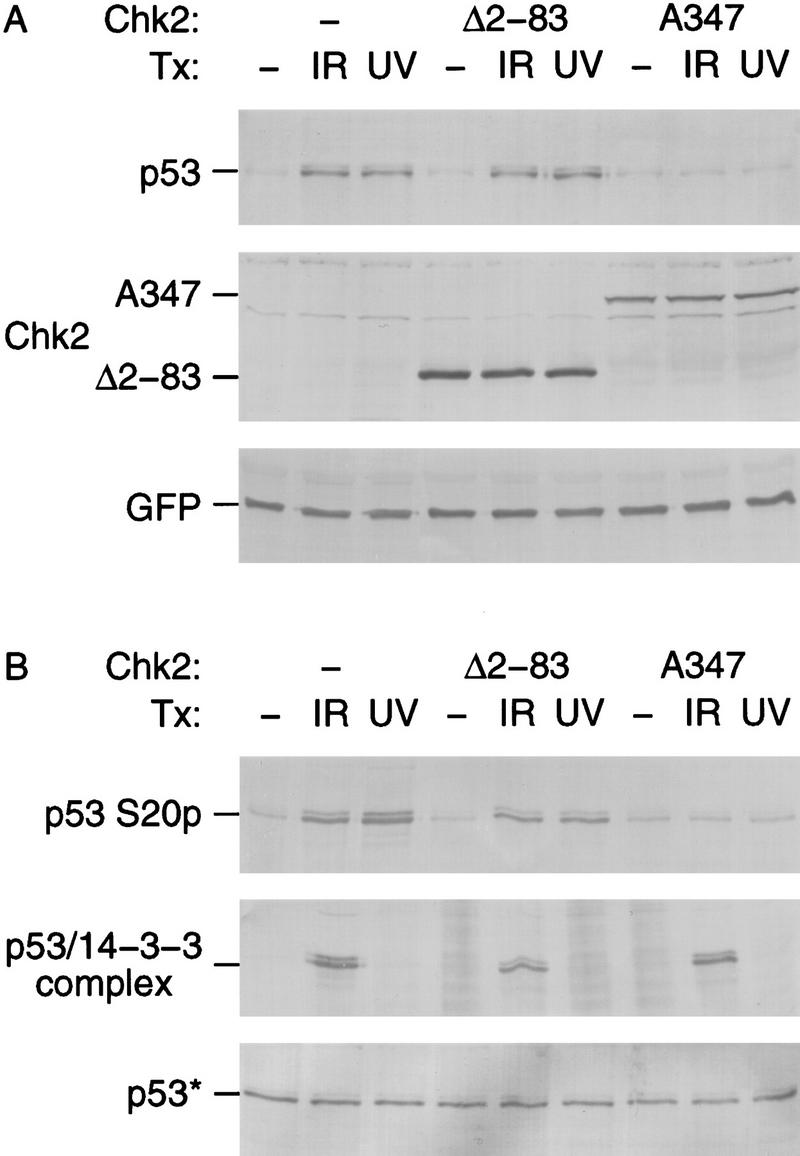
Dominant-negative Chk2/hCds1 mutants inhibit DNA damage-induced p53 stabilization (A) and Ser-20 phosphorylation (B). U2–OS cells were transiently transfected with plasmids expressing HA-tagged p53, the indicated Flag-tagged Chk2/hCds1 protein and GFP, as a marker of transfection efficiency. The cells were exposed to IR or UV light and cell extracts were prepared 2 and 16 hr later, respectively. (A) HA-tagged p53, Flag-tagged Chk2/hCds1, and GFP were resolved by denaturing gel electrophoresis and detected by immunoblotting. Equal levels of total protein were loaded in each lane to monitor the increase in p53 protein levels. (B) Phosphorylation of HA-tagged p53 on Ser-20 was monitored by immunoprecipitation with AbS20p, followed by immunoblotting with an antibody that recognizes the HA tag. The interaction of HA-tagged p53 with 14-3-3 proteins was monitored by immunoprecipitation with an antibody that recognizes 14-3-3 and detection of the coprecipitated HA-tagged p53 by immunoblotting. p53* indicates that to facilitate analysis of the p53 phosphorylation state and interaction with 14-3-3, the amounts of extract used in each lane of the top, middle, and bottom panels were adjusted so that all lanes had equal levels of total p53 (bottom; immunoblotting with an antibody that recognizes HA-tagged p53).
