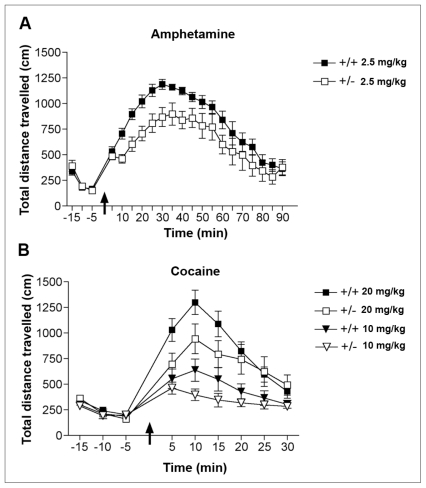
Fig. 4.
Blunted behavioural responses to stimulant drugs in adult dcc heterozygous (+/−) mice. (A) Mean (and standard error of the mean) locomotor activity before and after an injection of d-amphetamine sulfate (2.5 mg/kg, intraperitoneally; arrow) in adult male BL6 dcc +/− and wild-type (+/+) mice (n = 8 per group). Repeated-measures analysis of variance revealed a significant main effect of genotype. Reproduced with permission from Grant et al.83 (B) Mean (and standard error of the mean) locomotor activity before and after an injection of either 10 or 20 mg/kg, intraperitoneally, of cocaine hydrochloride (arrow) in adult male BL6 dcc +/− (n = 10 per group) and +/+ mice (low dose, n = 10; high dose, n = 12). A mixed-design, 3-way analysis of variance conducted on the first 25 minutes after cocaine injections revealed a significant main effect of genotype (F1,38 = 4.40, p = 0.042), but no significant genotype by dose interaction (p = 0.39).